Hi, what do you want to do?
EngageNY
Complex Numbers and Transformations
Your learners combine their knowledge of real and imaginary numbers and matrices in an activity containing thirty lessons, two assessments (mid-module and end module), and their corresponding rubrics. Centered on complex numbers and...
OpenStax
Open Stax: Kinematics in Two Dimensions: An Introduction
In this interactive module, students will observe that motion in two dimensions consists of horizontal and vertical components. They will understand the independence of horizontal and vertical vectors in two-dimensional motion.
Texas Education Agency
Texas Gateway: Kinematics in Two Dimensions: Section Summary
This is a summary of each of the sections in Chapter 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions of the AP Physics online text.
Other
Easyphysics: Chapter 5 Motion in Two Dimensions
Learners investigate motion in two dimensions. Some topics examined are two dimensional forces, gravity, and forces in three directions. The resource includes example problems with solutions and a chapter quiz.
Texas Education Agency
Texas Gateway: 3.1 Kinematics in Two Dimensions: An Introduction
By the end of this section, you will be able to observe that motion in two dimensions consists of horizontal and vertical components and understand the independence of horizontal and vertical vectors in two-dimensional motion.
Texas Education Agency
Texas Gateway: Glossary for Kinematics in Two Dimensions
This is a glossary of terms and definitions used in Chapter 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions of the AP Physics online text.
Texas Education Agency
Texas Gateway: Kinematics in Two Dimensions: Projectile Motion
By the end of this section, you will be able to identify and explain the properties of a projectile, such as acceleration due to gravity, range, maximum height, and trajectory; determine the location and velocity of a projectile at...
Physics Classroom
The Physics Classroom: Motion and Forces in Two Dimensions: Vector Addition
An extensive discussion of vector addition with links to interactives and exercises.
Texas Education Agency
Texas Gateway: Analyzing Two Dimensional Motion
Given descriptions, illustrations, graphs, charts, or equations, students will analyze motion in two dimensions, including projectile and circular motion.
OpenStax
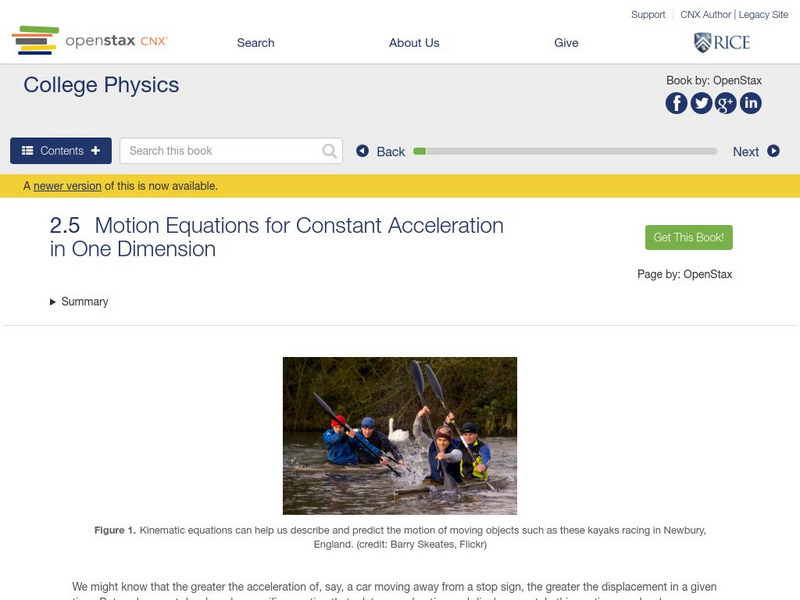
Open Stax: Physics: Motion Equations for Constant Acceleration in One Dimension
In this interactive module, students will calculate displacement of an object that is not accelerating, given initial position and velocity. They will also calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity,...
CK-12 Foundation
Ck 12: Circular Motion
[Free Registration/Login may be required to access all resource tools.] In the following lesson students will be asked to analyze and describe accelerated motion in two dimensions using equations including circular examples.
Georgia Department of Education
Ga Virtual Learning: Ap Physics 1: Two Dimensional Kinematics
In this interactive tutorial, students are introduced to motion in a second dimension, and model and predict the more complex motion of projectiles.
CK-12 Foundation
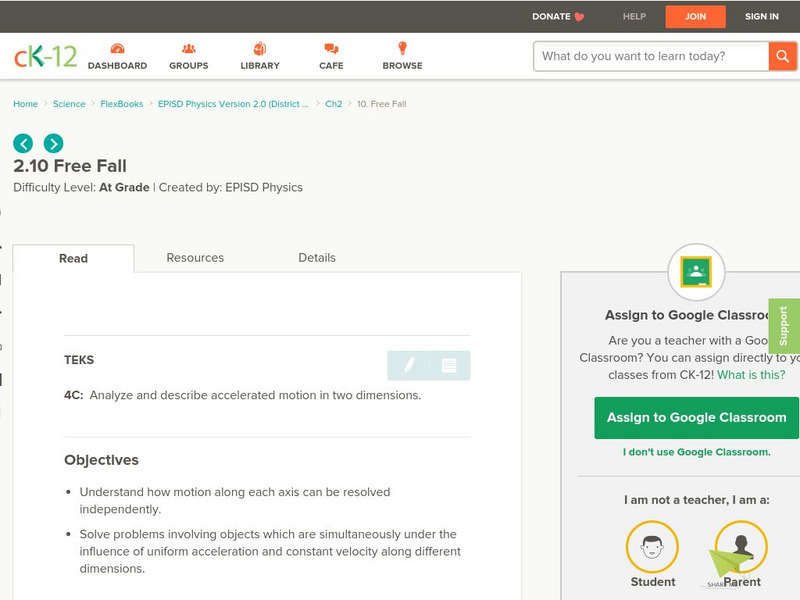
Ck 12: Episd: Free Fall
[Free Registration/Login may be required to access all resource tools.] Use this opportunity to understand accelerated motion in two dimensions, free fall.
CK-12 Foundation
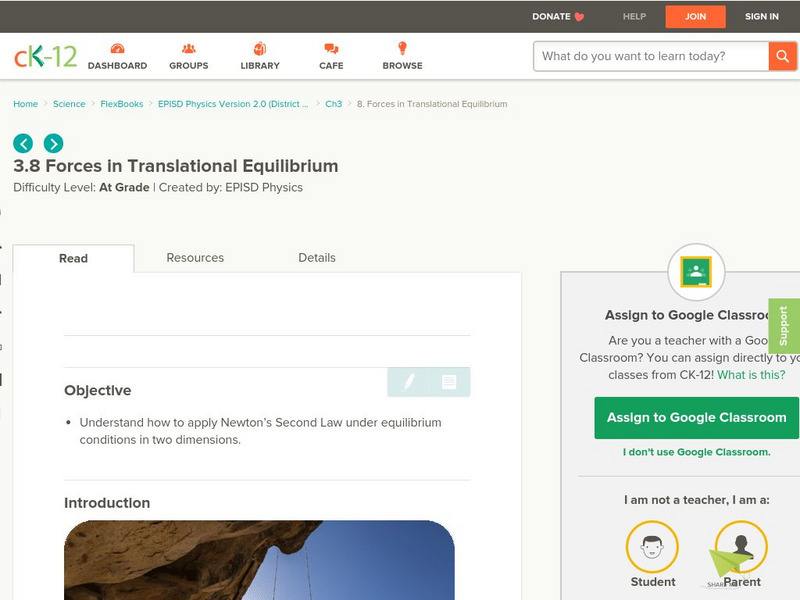
Ck 12: Forces in Translational Equilibrium
[Free Registration/Login may be required to access all resource tools.] The following tutorial helps students to understand how to apply Newton's Second Law under equilibrium conditions in two dimensions.
Texas Education Agency
Texas Gateway: Rotational Motion and Angular Momentum: Summary
This page provides a summary of each section in Chapter 10: Rotational Motion and Angular Momentum from the AP Physics online text.
CK-12 Foundation
Ck 12: Episd: Speed
[Free Registration/Login may be required to access all resource tools.] Understand what speed is and how to calculate it in one dimension motion.
American Museum of Natural History
American Museum of Natural History: O Logy: It's All Relative
Learn about the 4th dimensions and the theory of relativity.There is no absolute, or "same," time and space. This means time and space are different for everyone! How you experience events in time and space depends on two important...