Hi, what do you want to do?
Bozeman Science
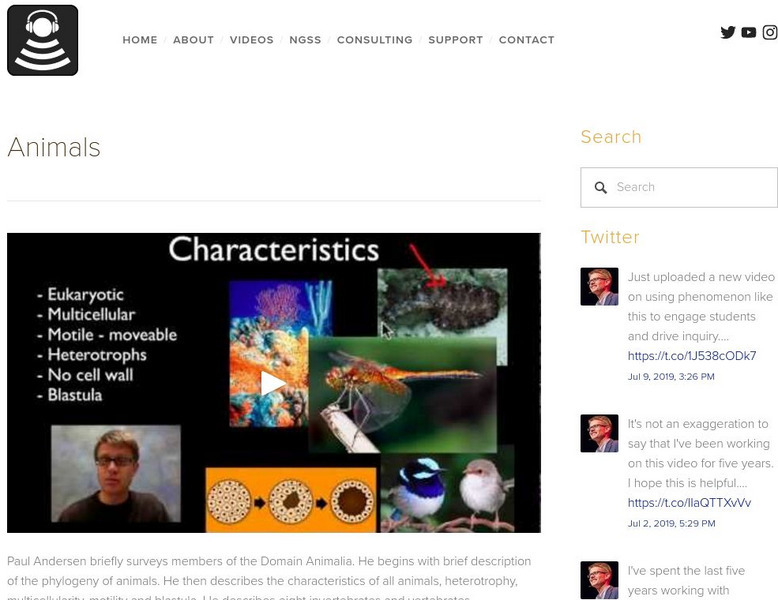
Bozeman Science: Animals
Paul Andersen briefly surveys members of the Domain Animalia. He begins with brief description of the phylogeny of animals. He then describes the characteristics of all animals, heterotrophy, multicellularity, motility and blastula. He...
Bozeman Science
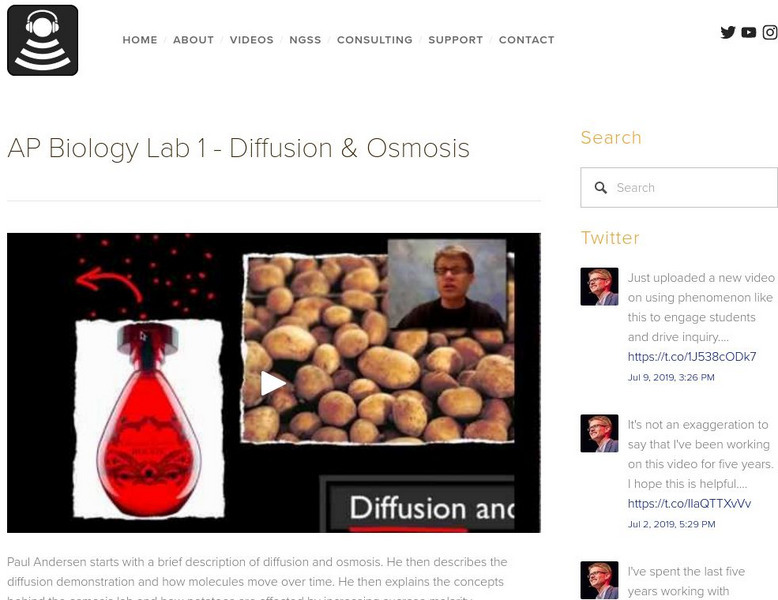
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Lab 1 Diffusion & Osmosis
Paul Andersen starts with a brief description of diffusion and osmosis. He then describes the diffusion demonstration and how molecules move over time. He then explains the concepts behind the osmosis lab and how potatoes are affected by...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Lab 10 Physiology of the Circulatory System
Paul Andersen shows you how to use a sphygmomanometer to measure the systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The the describes the elements of the laboratory portion. The temperature is gradually lowered and the respiration rate of a...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Lab 11 Animal Behavior
Paul Andersen introduces the concept of ethology and contrasts kinesis and taxis. He explains the importance of courtship rituals in fruit flies. He finally shows you how to use a choice chamber to study behavior in pill bugs.
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Lab 12 Dissolved Oxygen
Mr. Andersen demonstrates the azide-winkler method of dissolved oxygen analysis.
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Lab 2 Enzyme Catalysis
Paul Andersen starts with a brief description of enzymes and substrates. He then explains how you can measure the rate of an enzyme mediated reaction. Catalase from yeast is used to break hydrogen peroxide down into water and oxygen. He...
Bozeman Science
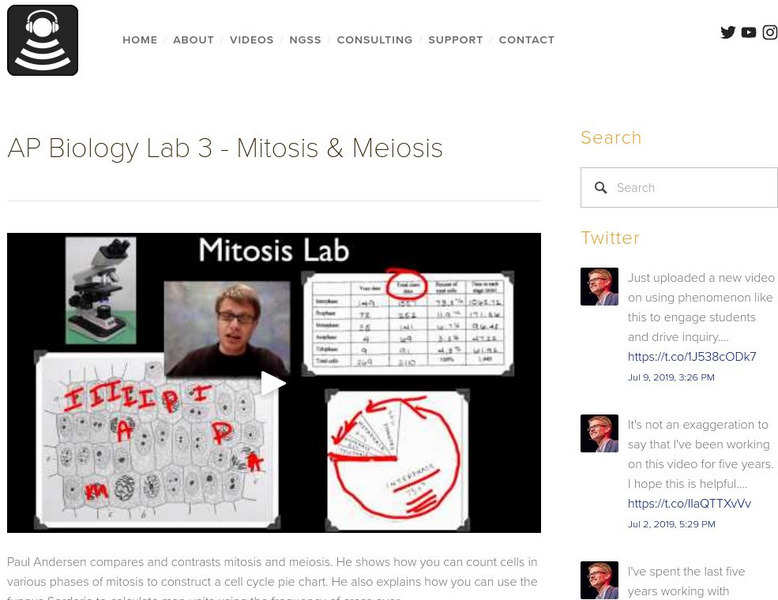
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Lab 3 Mitosis & Meiosis
Paul Andersen compares and contrasts mitosis and meiosis. He shows how you can count cells in various phases of mitosis to construct a cell cycle pie chart. He also explains how you can use the fungus Sordaria to calculate map units...
Bozeman Science
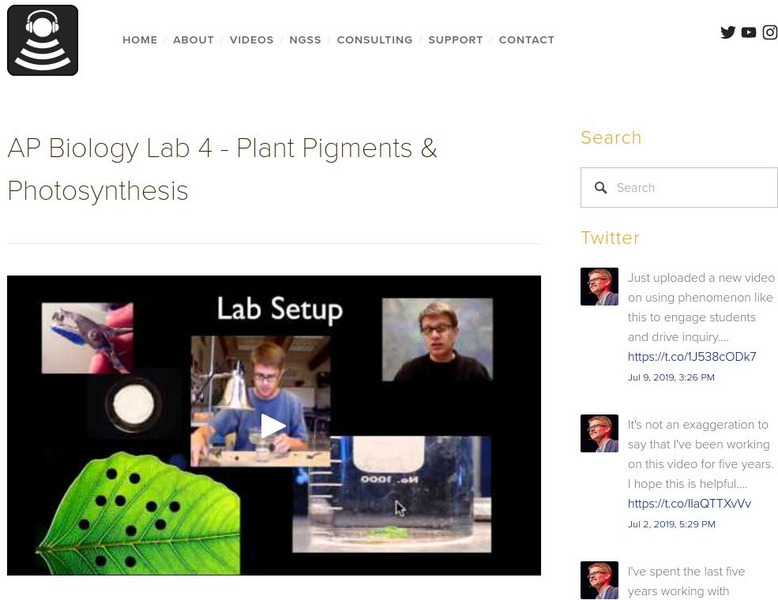
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Lab 4 Plant Pigments & Photosynthesis
Paul Andersen explains how pigments can be separated using chromatography. He shows how you can calculate the Rf value for each pigment. He then explains how you can measure the rate of photosynthesis using leaf chads and water...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Lab 5 Cellular Respiration
Paul Andersen explains how a respirometer can be used to measure the respiration rate in peas, germinating peas and the worm. KOH is used to solidify CO2 produced by a respiring organism.
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Lab 6 Molecular Biology
Paul Andersen explains the two major portions of the molecular biology lab in AP Biology. He starts by discussing the process of transformation. He explains how you can use the pGLO plasmid to produce glowing E. coli bacteria. He then...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Lab 7 Genetics of Drosophila
Mr. Andersen describes the virtual fly lab. Software at sciencecourseware.org allows for multiple matings and statistical analysis. [5:25]
Bozeman Science
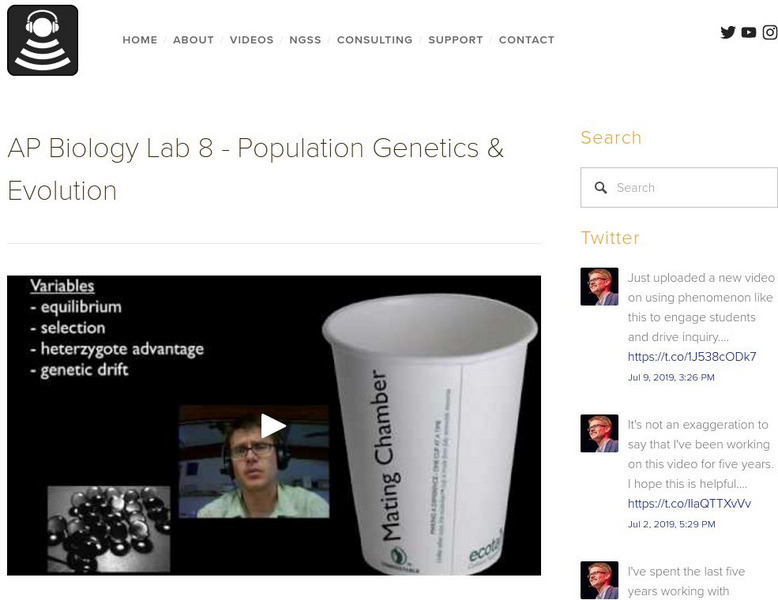
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Lab 8 Population Genetics & Evolution
Mr. Andersen explains Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and describes the bead lab. [6:00]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Lab 9 Transpiration
Paul Andersen starts by defining transpiration as evaporation off of a leaf. He then describes how a potometer can be used to measure the rate of transpiration in different environments.
Bozeman Science
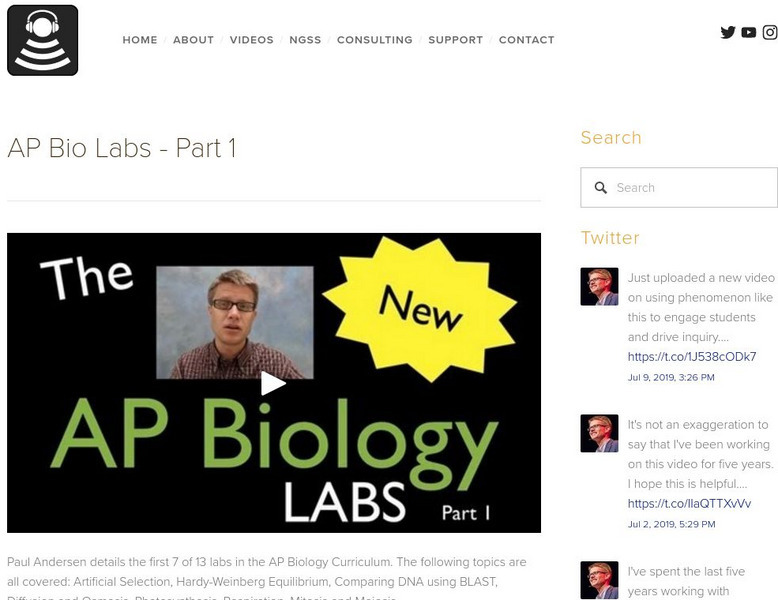
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Labs Part 1
Paul Andersen details the first 7 of 13 labs in the AP Biology Curriculum. The following topics are all covered: Artificial Selection, Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium, Comparing DNA using BLAST, Diffusion and Osmosis, Photosynthesis,...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Labs Part 2
Paul Andersen explains the final 6 of 13 AP Biology Labs. The following topics are included: Transformation, Restriction Analysis of DNA, Energy Dynamics, Transpiration, Animal Behavior, and Enzyme Activity.
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Biology Test: User Guide
Mr. Andersen describes the two portions of the AP Biology Test. Tips for answering multiple choice and free response questions are included. Sample questions from old AP tests are also included. [14:47]
Bozeman Science
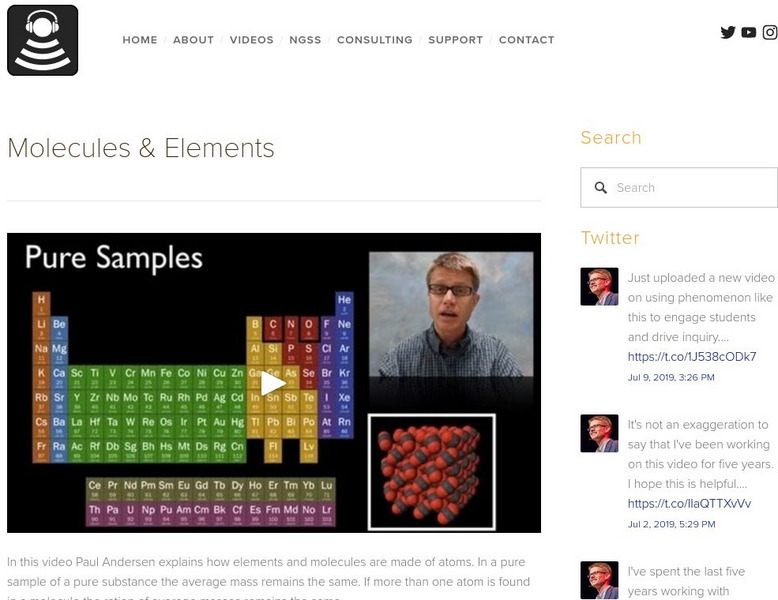
Bozeman Science: Ap Chemistry: Molecules & Elements
In this video, Paul Andersen explains how elements and molecules are made of atoms. In a pure sample of a pure substance the average mass remains the same. If more than one atom is found in a molecule the ration of average masses remains...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Chemistry: Chemical Analysis
In this video, Paul Andersen explains how chemical analysis is important in determining the composition, purity and empirical formula of a compound. An empirical formula determination problem is also included. [7:24]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Chemistry: The Mole
In this video, Paul Andersen defines and explains the importance of the mole. The mole is simply a number (like a dozen) used to express the massive number of atoms in matter. It serves as a bridge between the mass of a compound and the...
Bozeman Science
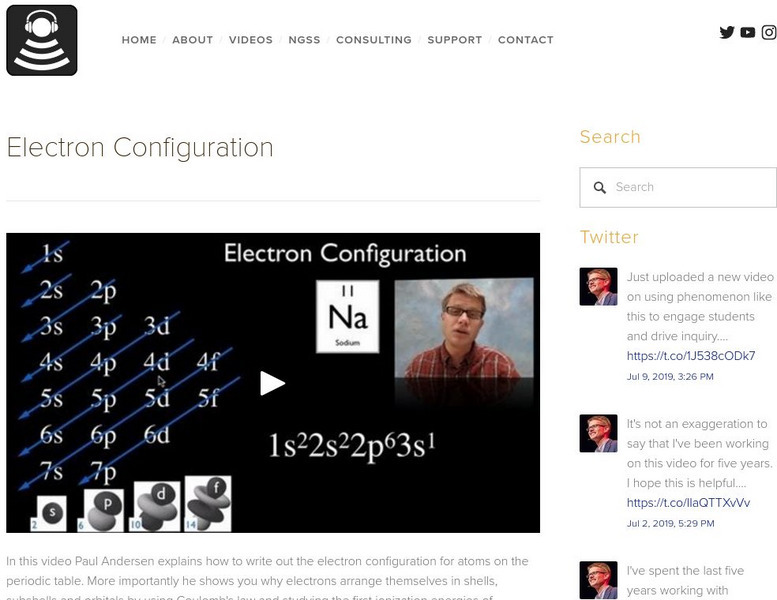
Bozeman Science: Ap Chemistry: Electron Configuration
In this video, Paul Andersen explains how to write out the electron configuration for atoms on the periodic table. More importantly he shows you why electrons arrange themselves in shells, subshells and orbitals by using Coulomb's law...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Chemistry: Periodicity
In this video, Paul Andersen explains why atoms in the periodic table show trends in ionization energy, atomic radii, electronegativity and charge. All of these trends are explained through Coulomb's Law. A brief description of Dmitri...
Bozeman Science
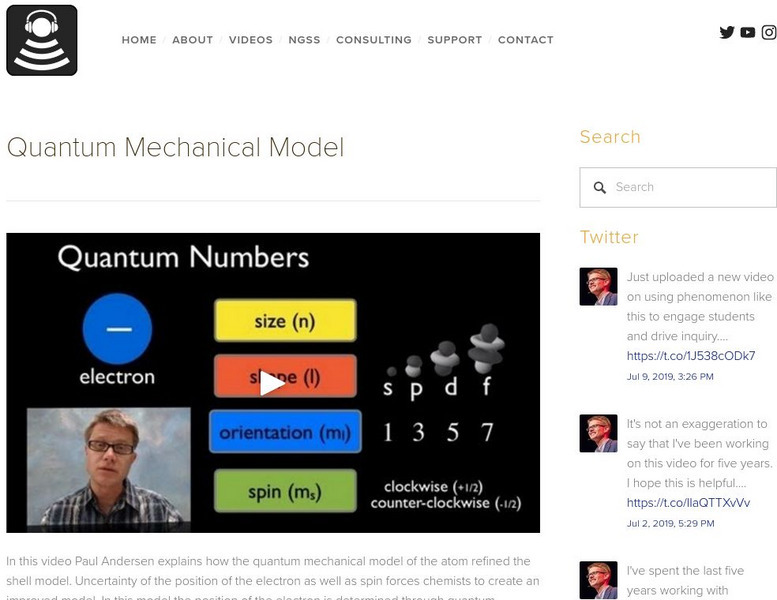
Bozeman Science: Ap Chemistry: Quantum Mechanical Model
Paul Andersen explains how the quantum mechanical model of the atom refined the shell model. Uncertainty of the position of the electron as well as spin forces chemists to create an improved model. In this model the position of the...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Chemistry: Atomic Models
Paul Andersen explains how the atomic model has changed over time. A model is simply a theoretical construct of phenomenon and so when we receive new data we may have to refine our model. Ionization energy data resulted in the formation...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Chemistry: Mass Spectrometry
In this video, Paul Andersen explains how a spectrometer was used to identify the presence of isotopes. This modified Dalton's original atomic theory because atoms of the same element had different masses. The functional parts of a mass...