Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Specular Reflection
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how light that is perfectly reflected creates specular reflection. The angle of the incident ray is equal to the angle of the reflected ray. Specular reflection is also known as mirror-like...
Bozeman Science
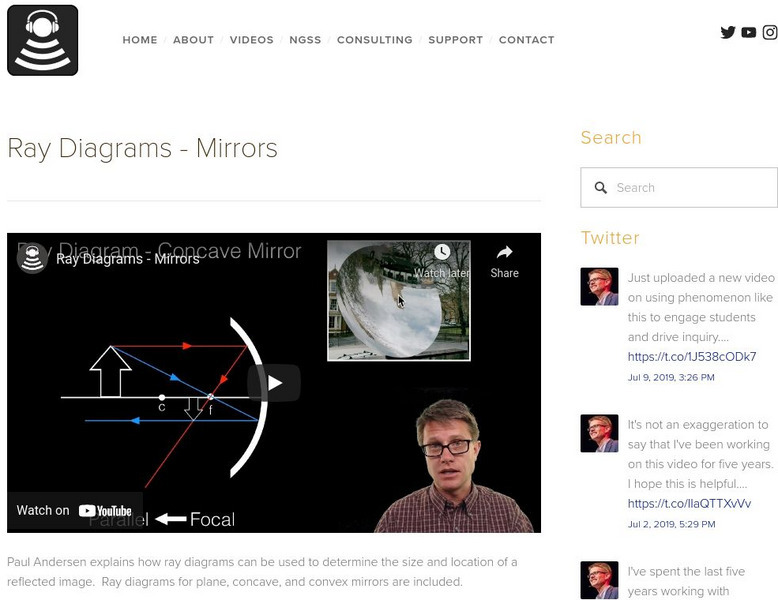
Bozeman Science: Physics: Ray Diagrams Mirrors
In this video, Paul Andersen explains how ray diagrams can be used to determine the size and location of a reflected image. Ray diagrams for plane, concave, and convex mirrors are included. [11:44]
Bozeman Science
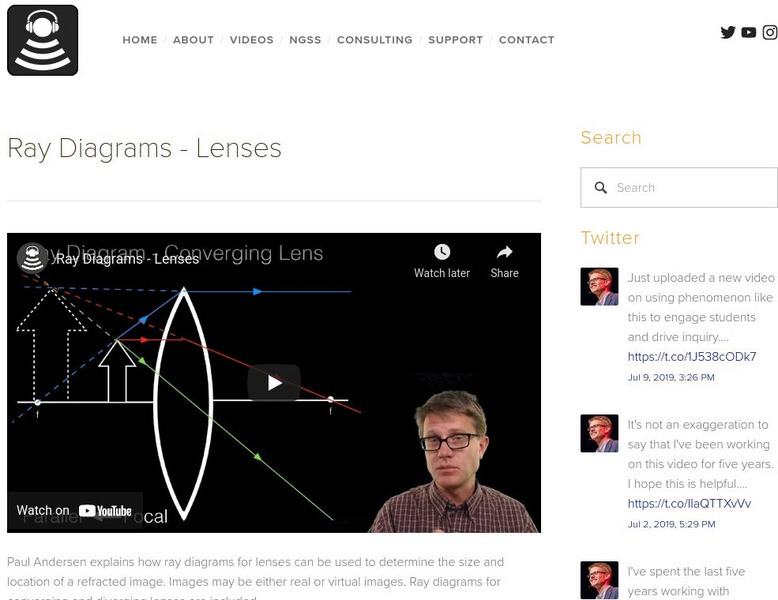
Bozeman Science: Physics: Ray Diagrams Lenses
In this video, Paul Andersen explains how ray diagrams for lenses can be used to determine the size and location of a refracted image. Images may be either real or virtual images. Ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses are...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Electromagnetic Waves
In the following video Paul Andersen details the characteristics of electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves that can move through both mediums and vacuums. The electric and magnetic fields oscillate...
Bozeman Science
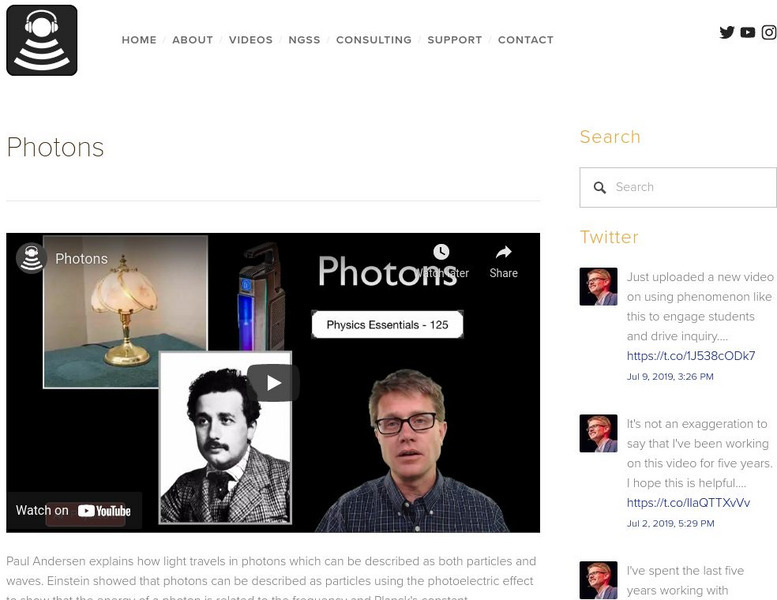
Bozeman Science: Photons
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how light travels in photons which can be described as both particles and waves. Einstein showed that photons can be described as particles using the photoelectric effect to show that the...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Matter as a Particle
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how matter, like light, can be treated as both a particle and a wave. Louis de Broglie proposed that matter could act as a wave and described the wavelength of matter as a function of...
Bozeman Science
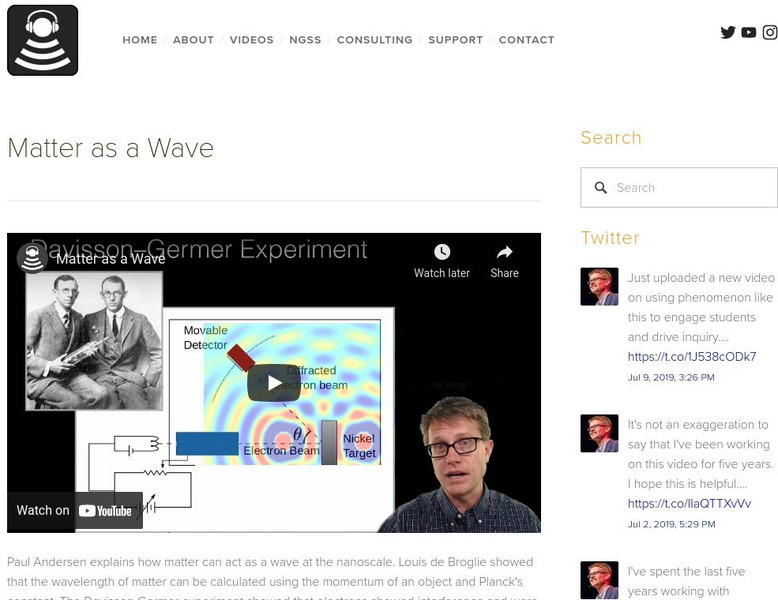
Bozeman Science: Matter as a Wave
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how matter can act as a wave at the nanoscale. Louis de Broglie showed that the wavelength of matter can be calculated using the momentum of an object and Planck's constant. The...
Bozeman Science
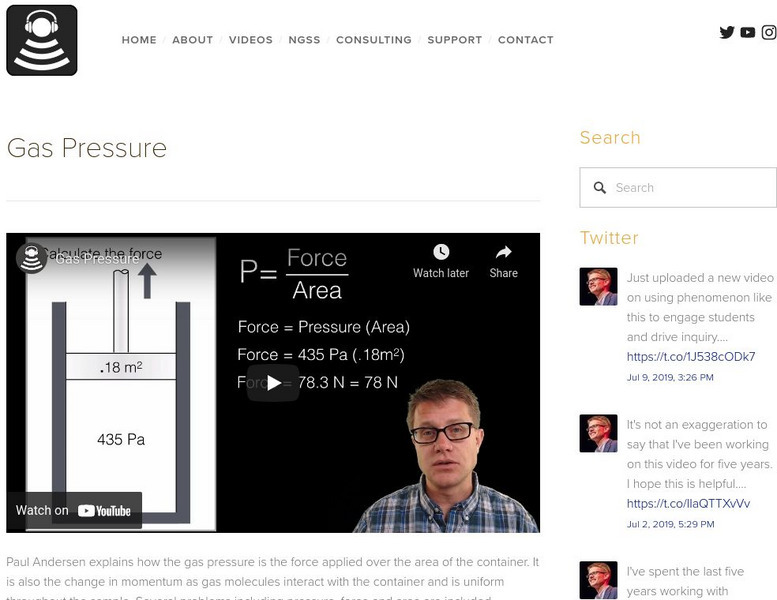
Bozeman Science: Gas Pressure
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how the gas pressure is the force applied over the area of the container. It is also the change in momentum as gas molecules interact with the container and is uniform throughout the sample....
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Kinetic Theory & Temperature
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how the macroscopic measure of temperature can be related to the average kinetic energy of molecules in motion. The Boltzmann constant and distribution can be used to calculate the root mean...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ideal Gas Law
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how the pressure, volume, amount, and temperature of an ideal gas are related. Absolute zero of a gas can be determined by varying the temperature and measuring the corresponding volume of a...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Thermal Equilibrium
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how objects in contact with varying temperatures will eventually reach thermal equilibrium with equal temperatures. The amount of thermal energy transferred is related to the mass and...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Second Law of Thermodynamics
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how the second law of thermodynamics applies to reversible and irreversible processes. In a reversible process the net change in entropy is zero. In and irreversible process the entropy will...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Wave Function
In this video Paul Andersen explains how the location of matter can be determined at the nanoscale using the wave function. The absolute value of the wave function can be used to determine the probability of finding matter in a location....
Bozeman Science
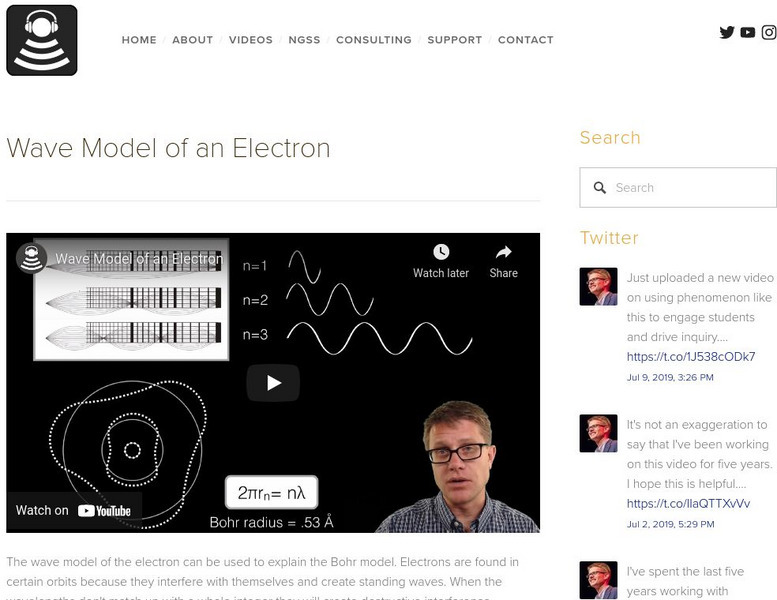
Bozeman Science: Wave Model of an Electron
In the following video the wave model of the electron can be used to explain the Bohr model. Electrons are found in certain orbits because they interfere with themselves and create standing waves. When the wavelengths don't match up with...
Bozeman Science
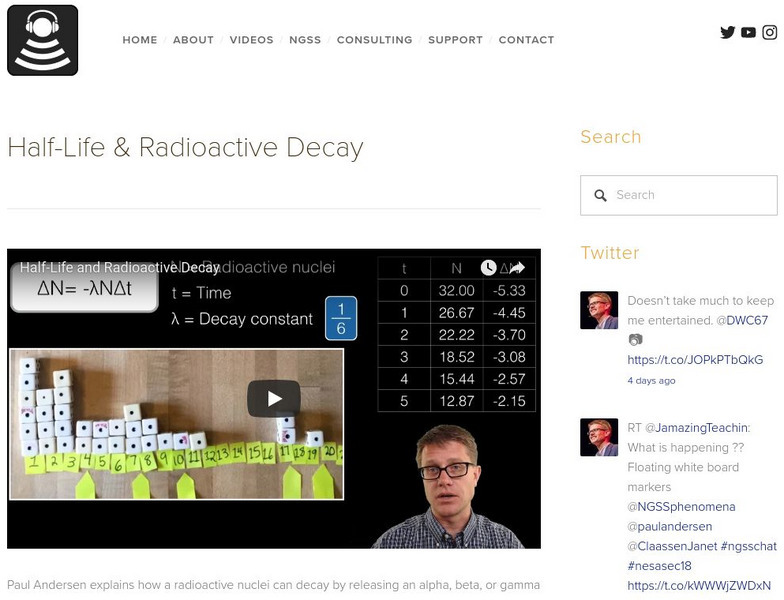
Bozeman Science: Half Life & Radioactive Decay
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how a radioactive nuclei can decay by releasing an alpha, beta, or gamma particle. The exact moment of decay for each nuclei can not be determined but probability is useful in predicting the...
Bozeman Science
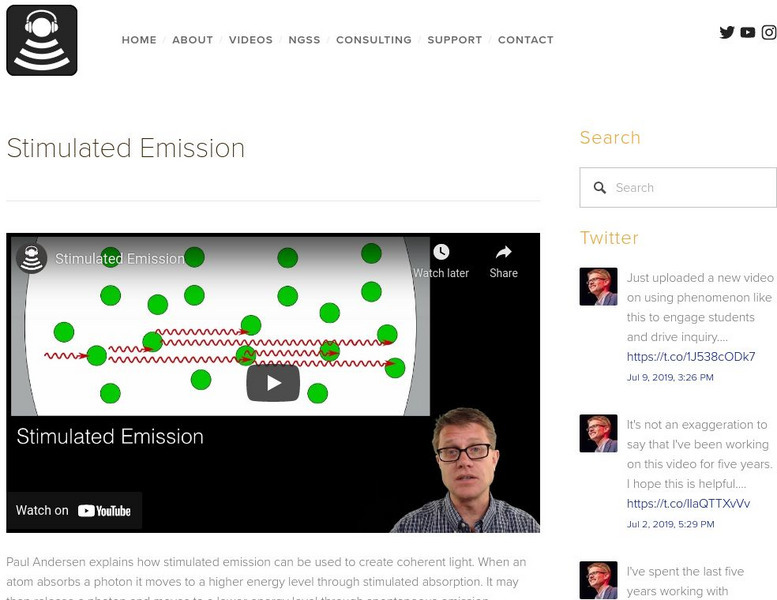
Bozeman Science: Stimulated Emission
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how stimulated emission can be used to create coherent light. When an atom absorbs a photon it moves to a higher energy level through stimulated absorption. It may then release a photon and...