Bozeman Science
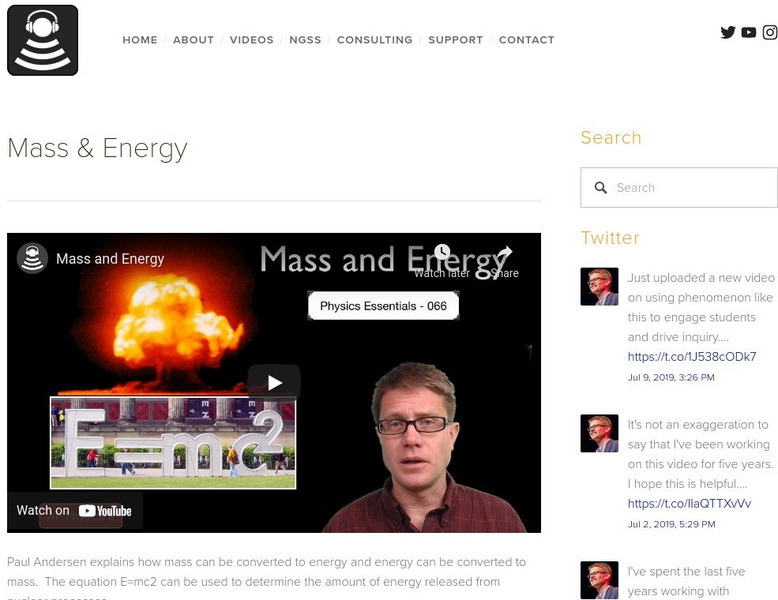
Bozeman Science: Mass and Energy
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how mass can be converted to energy and energy can be converted to mass. [3:30]
Bozeman Science
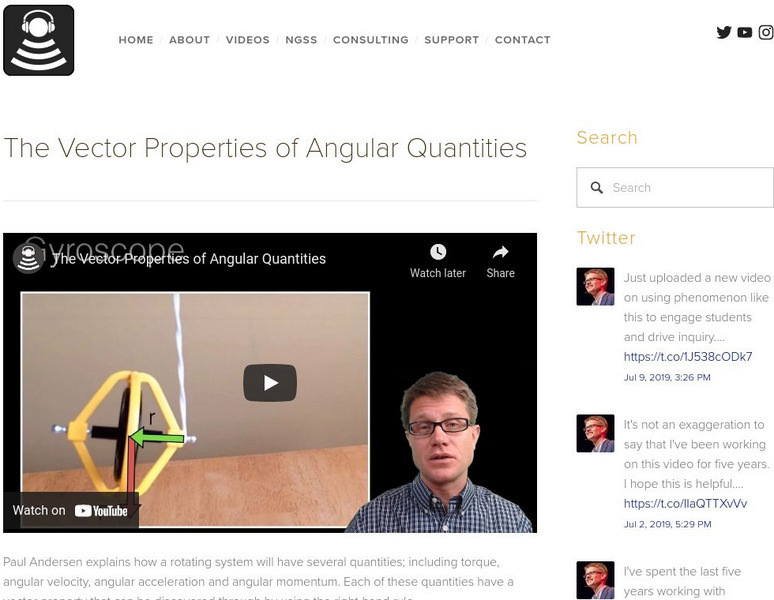
Bozeman Science: The Vector Properties of Angular Quantities
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how a rotating system will have several quantities; including torque, angular velocity, angular acceleration and angular momentum. [7:15]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Angular Momentum of a System
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how the angular momentum of a system can be calculated by determining the angular momentum of all individual objects within the system. [6:34]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Angular Impulse
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how the change in angular momentum is equal to the torque applied over a given time. [4:54]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Magnetic Properties
The following video explains how all material has magnetic properties. Ferromagnetic material can be permanently magnetized, paramagnetic material will align with magnetic fields, and diamagnetic material will align weakly with magnetic...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Electromagnetic Induction
The following video narrated by Paul Anderson explains how electromagnetic induction occurs when the magnetic flux of an object changes. The magnetic flux is product of the surface area perpendicular to the magnetic field and the...
Bozeman Science
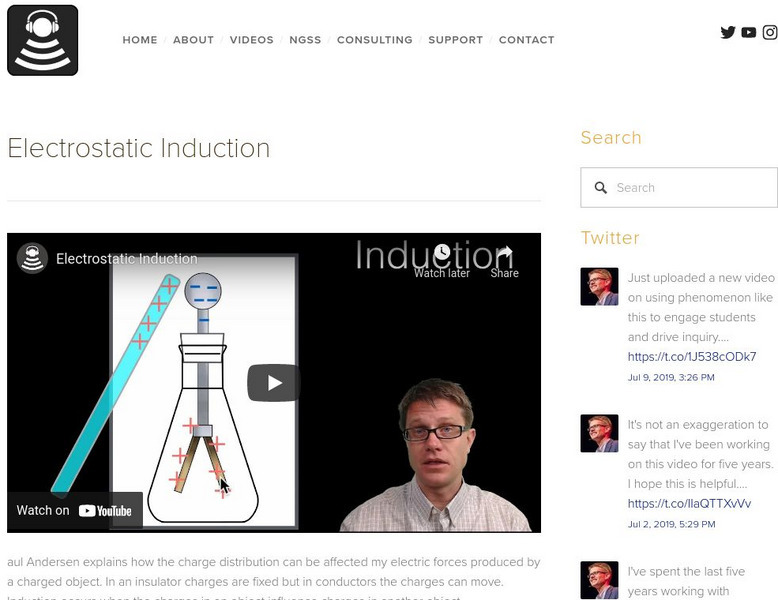
Bozeman Science: Electrostatic Induction
This video narrated by Paul Andersen explains how the charge distribution can be affected my electric forces produced by a charged object. In an insulator charges are fixed but in conductors the charges can move. Induction occurs when...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Resistors and Capacitors
The following video narrated by Paul Andersen explains how resistors and capacitors affect circuits. The resistance of a resistor is affected by the resistivity of the material and the geometry of the resistor. The current through a...
Bozeman Science
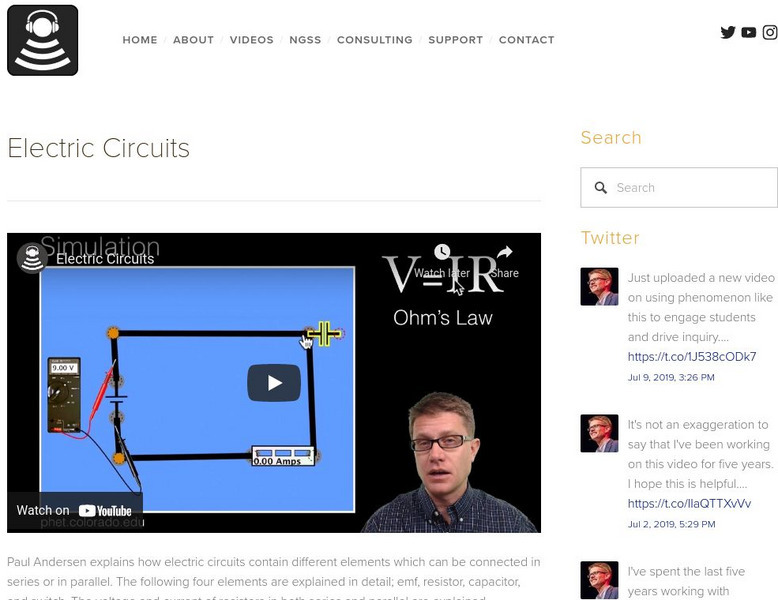
Bozeman Science: Electric Circuits
The following video narrated by Paul Andersen explains how electric circuits contain different elements which can be connected in series or in parallel. The following four elements are explained in detail; emf, resistor, capacitor, and...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Systems
The following video narrated by Paul Andersen explains how systems are two or more objects that interact with one another. If a system has no relevant internal structure it can be treated as an object. The conservation laws apply to...
Bozeman Science
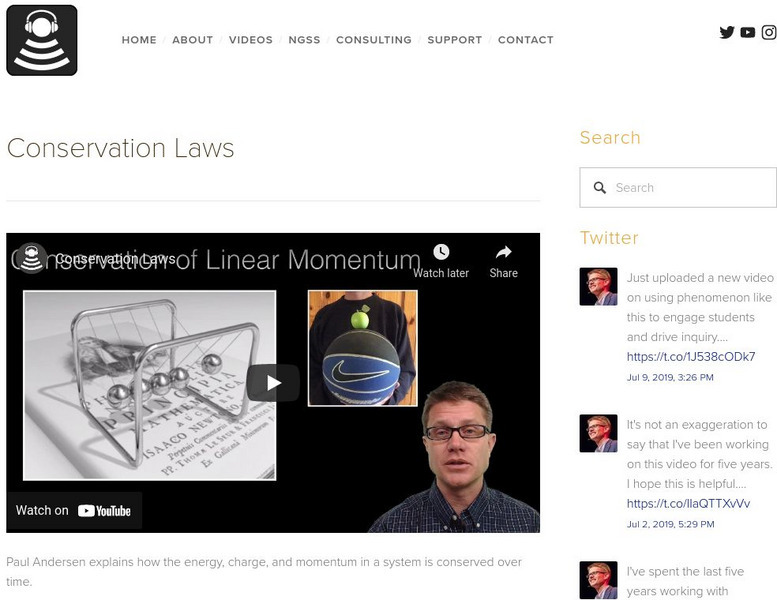
Bozeman Science: Conservation Laws
The following video narrated by Paul Andersen explains how the energy, charge, and momentum in a system is conserved over time. [4:53]
Bozeman Science
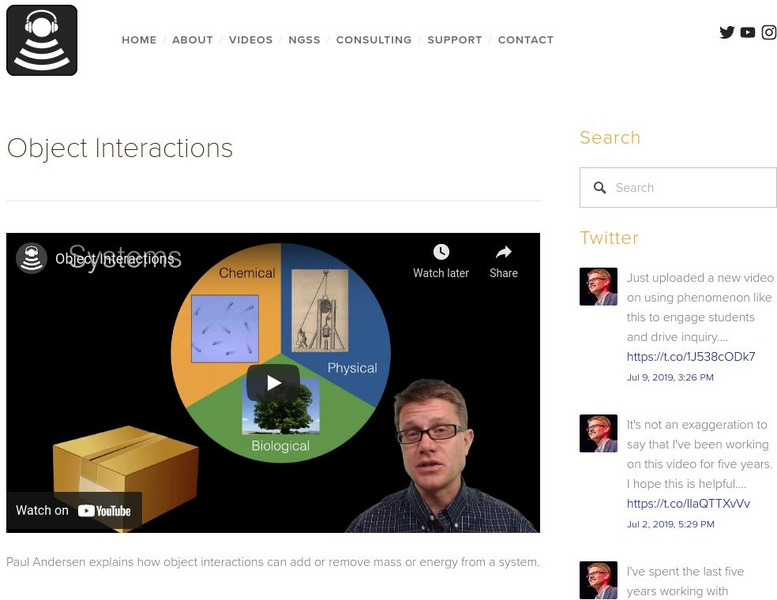
Bozeman Science: Object Interactions
The following video narrated by Paul Andersen explains how object interactions can add or remove mass or energy from a system. [2:14]
Bozeman Science
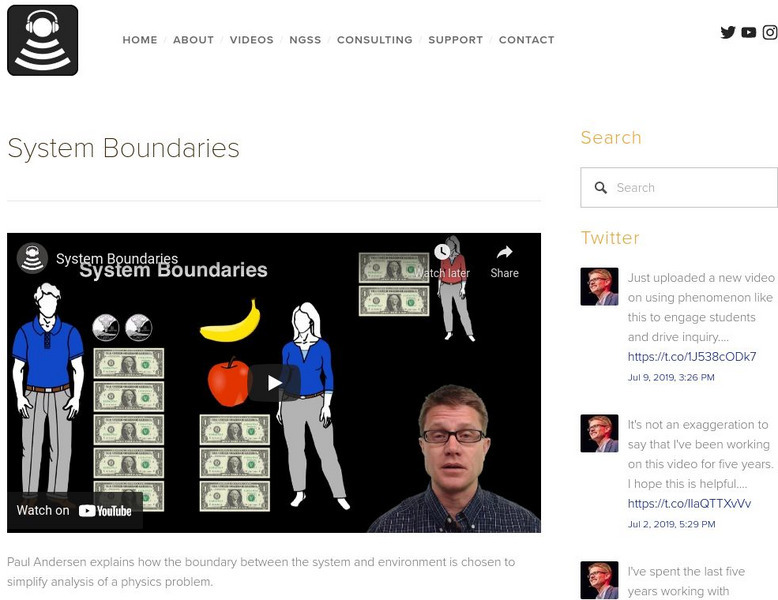
Bozeman Science: System Boundaries
In this video Paul Andersen explains how the boundary between the system and environment is chosen to simplify analysis of a physics problem. [3:13]
Bozeman Science
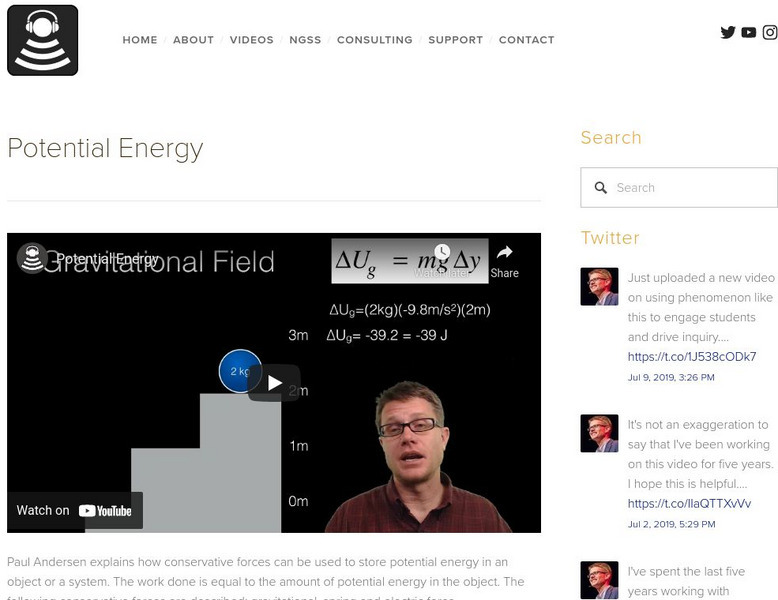
Bozeman Science: Potential Energy
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how conservative forces can be used to store potential energy in an object or a system. The work done is equal to the amount of potential energy in the object. The following conservative...
Bozeman Science
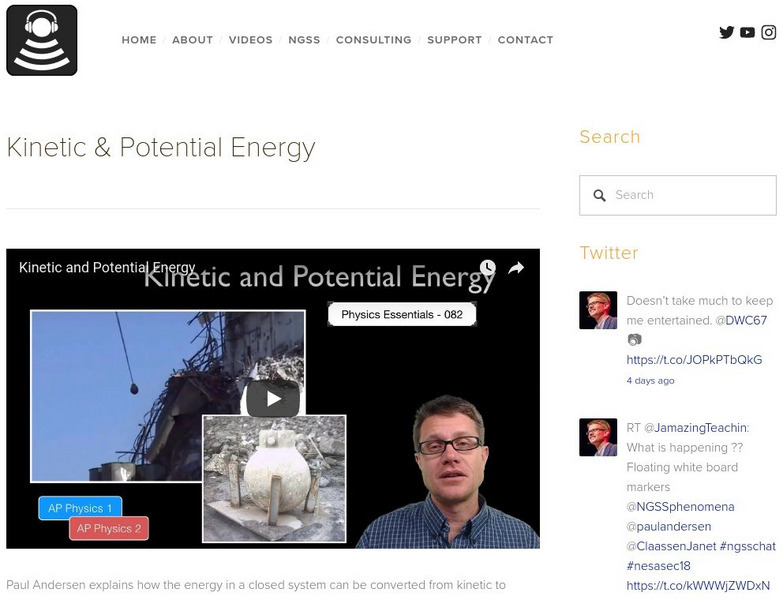
Bozeman Science: Kinetic and Potential Energy
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how the energy in a closed system can be converted from kinetic to potential to kinetic energy. Sample problems and a simulation is contained. [4:46]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Work and Power
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how the work is a product of the external force applied to an object or system and the distance it moves. Power is a measure of the amount of work done per unit time. [6:45]
Bozeman Science
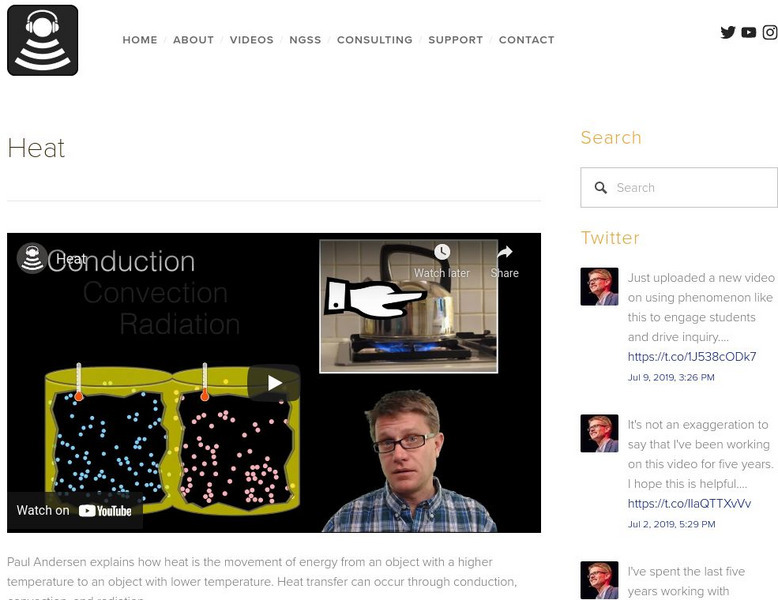
Bozeman Science: Heat
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how heat is the movement of energy from an object with a higher temperature to an object with lower temperature. Heat transfer can occur through conduction, convection, and radiation. [4:10]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Thermodynamics and P v Diagrams
In this video Paul Andersen explains how the First Law of Thermodynamics applies to an ideal gas in a piston. A pressure-volume graph can be used to determine the type of thermodynamic process. Included is a discussion of and P-V diagram...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Emission or Absorption Spectra
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how the photons emitted from or absorbed by an atom or nuclei is directly related to electrons moving between energy level. Absorption and emission are a direct result of the conservation of...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Physics: Kirchhoff's Loop Rule
In this, video Paul Andersen explains how Kirchhoff's Loop Rule can be used to calculate the voltage of different components of a circuit. The sum voltage throughout an entire loop will sum to zero following the law of conservation of...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Bernoulli's Equation
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how Bernoulli's Equation describes the conservation of energy in a fluid. The equation describes the pressure energy, potential energy, and kinetic energy of a fluid at a single point. A...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Energy Mass Equivalence
Paul Andersen explains how the law of conservation of energy applies to both energy and mass. Einstein showed that mass and energy are equivalent and that the amount of energy contained within matter can be calculated using the famous...
Bozeman Science
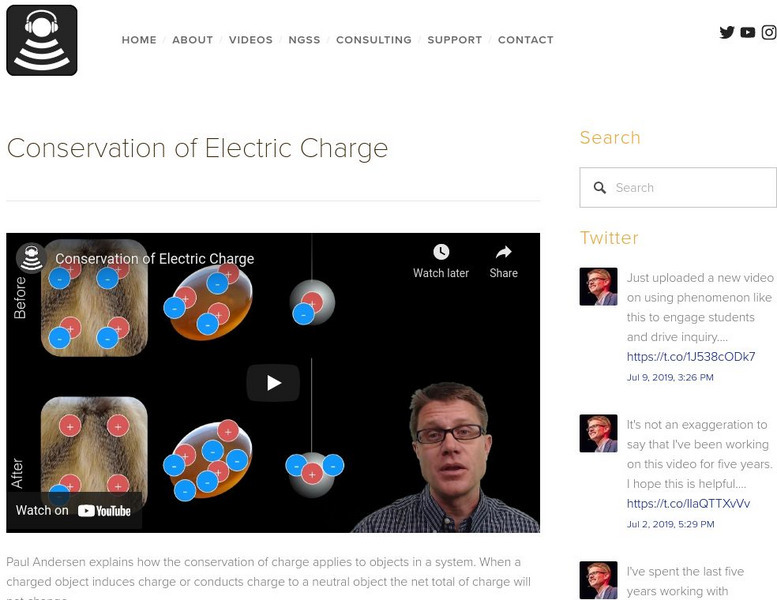
Bozeman Science: Physics: Conservation of Electric Charge
In this video, Paul Andersen explains how the conservation of charge applies to objects in a system. When a charged object induces charge or conducts charge to a neutral object, the net total of charge will not change. [6:07]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Physics: Kirchhoff's Junction Rule
In this video, Paul Andersen explains how Kirchhoff's Junction Rule can be applied to series and parallel circuits. Kirchhoff's Junction Rule is an application of the conservation of charge. The current into a junction will always equal...