Bozeman Science
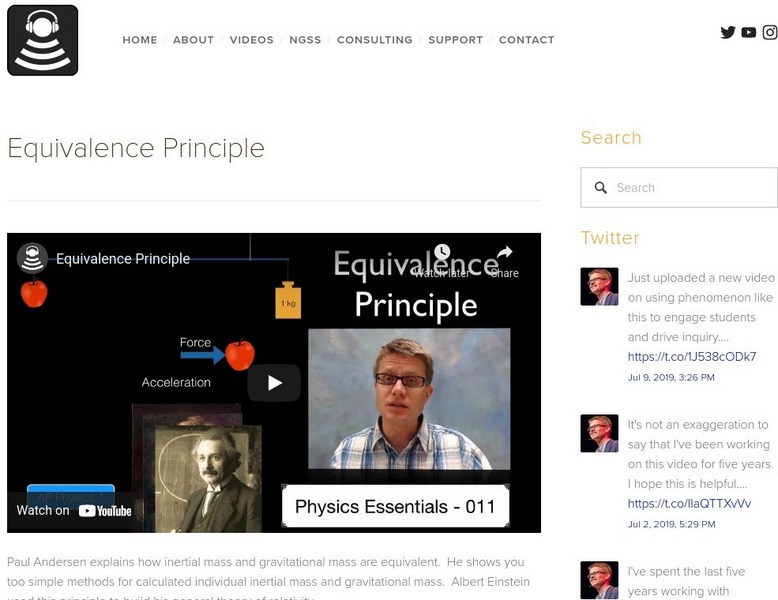
Bozeman Science: Equivalence Principle
Paul Andersen explains how inertial mass and gravitational mass are equivalent. [6:16]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Resistivity
Paul Andersen explains how the resistivity of a material opposes the flow of charge. [4:22]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Vector Field
Paul Andersen explains how a vector field shows the distribution of vector quantities. [7:47]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Gravitational Force
Paul Andersen explains how an object with mass placed in a gravitational field experiences a gravitational force. [5:01]
Bozeman Science
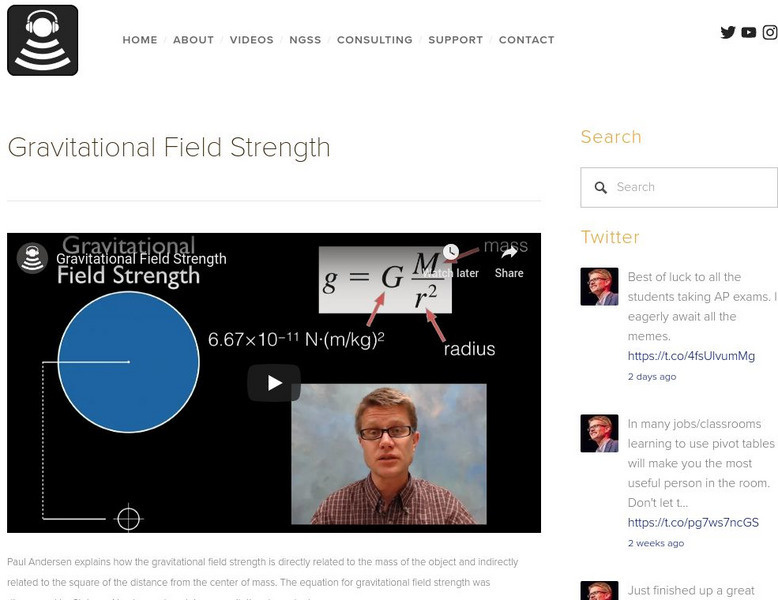
Bozeman Science: Gravitational Field Strength
Find out how the gravitational field strength is directly related to the mass of the object and indirectly related to the square of the distance from the center of mass. [5:38]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Motion
Mr. Andersen describes motion as the movement of an object over time. An experiment in motion is used to calculate velocity and acceleration of a tennis ball. [8:46]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Forces
A video reviewing over how forces are pushes or pulls on an object. Learn how forces can be determined by measuring the motion of an object. Also, how an objects acceleration can show that a force is present. [5:47]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Interaction Forces
Mr. Anderson illustrates the concept that forces on an object always require another object, and that an object cannot exert a force on itself. If net forces on an object are balanced the object will remain at rest or move with a...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Vector Sum of Forces
Paul Andersen explains how the vector sum of forces can be used to identify the net force on an object. The net force can be used to determine the overall acceleration of the object using Newton's Second Law. [6:54]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Simple Harmonic Motion
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how simple harmonic motion occurs when a restoring force returns an object toward equilibrium. The two types of harmonic motion studied in AP Physics are the mass spring oscillator and the...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Contact Forces
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how contact forces result from interatomic forces. [5:29]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Momentum
In the following video Paul Andersen will first define momentum as the product of an object's mass and velocity. 3.56]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Impulse
In the following video Paul Andersen defines impulse as the product of the force applied and the time over which the force is applied. The impulse of an object is equivalent to the change in momentum of the object. [9:11]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Work Energy Principle
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how the kinetic energy gained by an object is equivalent to the work done on the object. The force on the object must act parallel or antiparallel to the motion of the object to do work. [8:12]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Torque
In the following video Paul Andersen begins by discriminating between translation and rotational motion. He then explains how a torque is the product of the lever arm and the force perpendicular. [7:03]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Rotational Motion
Physics video [10:40] from science teacher, Paul Andersen, in which he teaches us the concept of rotational force through images and formulas using clear and understandable explanations.
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Angular Momentum
Video [7:28] in which Paul Andersen explains in a clear and understandable way, that rotating objects have angular momentum.
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Gravitational Forces
Award-winning science teacher Paul Andersen helps make physics understandable as he explains how gravitational forces differ from the other three fundamental forces: electromagnetic, and strong and weak nuclear forces. [5:05]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Physics Essentials 58: Motion of the Center of Mass
Award winning science teacher, Paul Andersen, explains how linear motion of an object can be measured using the center of mass in this interesting and informative video [4:46]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Position, Velocity & Acceleration
In the following video Paul Andersen explains for the position of an object over time can be used to calculate the velocity and acceleration of the object. If a net force acts on a object it will experience an acceleration. [7:55]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Linear Momentum
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how the linear momentum is equal to the product of the mass of an object and the velocity of the center of mass. He uses video analysis software to calculate the velocity of an object and...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Force Time Graph
In the following video Paul Andersen explains hot the force-time graph can be used to determine the impulse of an object. Since the impulse and the change in momentum are equivalent the graph can also be used to determine the change in...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Total Energy
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how the total energy of a system is the combination of kinetic, potential and internal energy of the objects. He then shows you how to calculate the kinetic energy, gravitational potential...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Heating
In the following video Paul Andersen explains how heating is the transfer of energy (heat) from a warmer object to a cooler object. Heat can be transferred through conduction, convection and radiation. At the microscopic level conduction...