Hi, what do you want to do?
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Market Equilibrium
Practice what you've learned about finding equilibrium price and quantity both intuitively and graphically in this exercise.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Price Ceilings and Price Floors
This article discusses how quantity demanded react to artificial constraints on price.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Market Equilibrium
The actual price you see in the world is a balancing act between supply and demand.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Lesson Summary: Long Run Self Adjustment in the Ad as Model
In this lesson summary review, remind yourself of the key terms and graphs related to the long-run self-adjustment mechanism. The long-run self-adjustment mechanism is one process that can bring the economy back to "normal" after a...
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Law of Supply
If the price of something goes up, companies are willing (and able) to produce more of it.
Curated OER
Monopolistically Competitive Firm in Long Run Equilibrium
This site uses interactive graphs to show how changes in demand would change a firm's output, price, and profits or losses in a monopolistically competitive market structure.
Curated OER
Labor Market Equilibrium With a Payroll Tax
This site provides a good analysis of the concepts of marginal product, marginal revenue product, marginal costs, and how a monopsonist determines wages and quantity of labor hired.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Mit: Open Course Ware: Intermediate Microeconomic Theory
An intermediate level course in microeconomics from MIT. Includes suggested readings, lecture notes, assignments, and exams.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Shifts in Aggregate Supply
If either the aggregate supply or aggregate demand curve shifts in the aggregate demand/aggregate supply-AD/A-model, the original equilibrium in the AD/AS diagram will shift to a new equilibrium. Increases and decreased in the price of...
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Externalities: Foundational Concepts
Practice what you have learned about identifying externalities and using graphs to identify both market equilibrium and socially optimal outcomes in this exercise.
Council for Economic Education
Econ Ed Link: The Prices Are Changing
This instructional activity will help students to understand how markets are created by the interaction of buyers and sellers, what demand and supply are, what equilibrium price is, and how demand and supply interact with price changes.
Other
Online Texts: Monopolistic Competition: Demand Change
This site uses graphs to show how changes in demand would change a firm's output, price, and profits or losses in a monopolistically competitive market structure.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Economic Efficiency
Read about consumer surplus, producer surplus, and deadweight loss. Did you know that demand and supply diagrams can help us understand more than supply and demand curves and equilibrium? They can also help us understand economic...
Council for Economic Education
Econedlink: Profit Video and Quiz
This video teaches the concept of Profit. Profit is income received for entrepreneurial skills or risk taking and is calculated by subtracting a firm's costs of producing a good or service from the revenues received from selling the good...
Other
South Western Learning: Econ News: Comparative Statics: Perfect Competition
This site offers economics-based newspaper headlines and asks follow-up questions based on supply and demand in a perfectly competitive market.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Law of Demand
If the price of something goes up, people are going to buy less of it.
Texas Education Agency
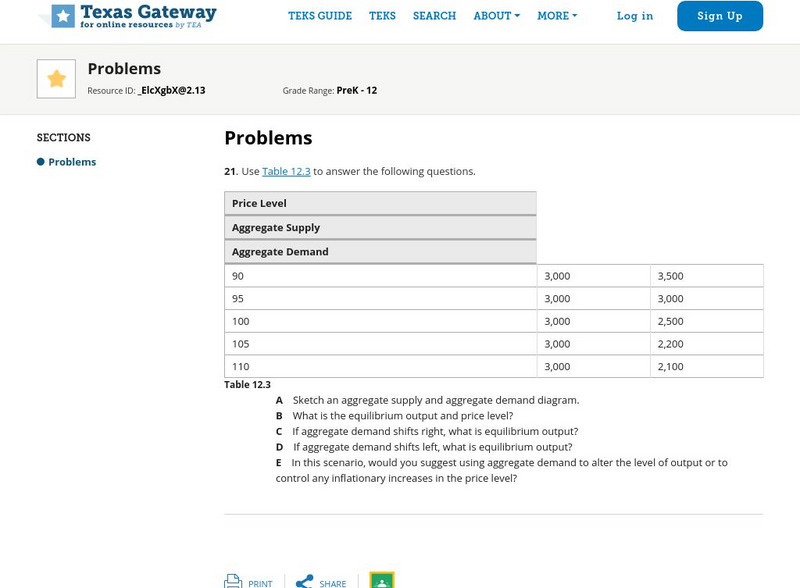
Texas Gateway: Chapter 12: Neoclassical Perspective: Problems
This section provides 5 problems to solve pertaining to the information presented in Chapter 12: Neoclassical Perspective.
Curated OER
Model of Monopolistic Competition
This site uses an example of "pushcarts on the beach" to demonstrate a monopolistically competitive market structure and how as more firms enter the market, price, quantity, and deadweight loss are all effected.
Council for Economic Education
Econ Ed Link: Henry Ford and the Model T: A Case Study in Productivity (Part 3)
Henry Ford's use of mass production strategies to manufacture the Model T revolutionized industrial manufacturing. This 3-part learning unit provides students with the story of Henry Ford and the Model T from an economics perspective....
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: The Expenditure Output, or Keynesian Cross, Model
Use a diagram to analyze the relationship between aggregate expenditure and economic output in the Keynesian model.