Physics Aviary
Physics Aviary: Thomson's Cathode Ray Tube Lab
This lab is designed to have students look at the deflection of a cathode ray beam using magnetic fields and electric fields.
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Duchenne Machine 1850
French physician Guillaume Benjamin Amand Duchenne invented a device that electrically stimulates muscles. The apparatus gave him new insight into neuromuscular disorders, earned him the epitaph of "father of electrotherapeutics," and...
Orpheus Books
Q Files: Electricity and Magnetism: Electric Charge
Learn how electric charges work and about Coulomb's Law, which is used to calculate the strength of an electric force.
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Arc Lamp 1876
Fire lighted the night for many centuries. Then came Sir Humphry Davy and the birth of the arc lamp, an invention built upon in the years that followed by many.
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Magnetometer 1832
The Earth, the moon, the stars and just about everything in between has a magnetic field, and scientists use magnetometers when they need to know the strength of those fields.
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Bell Telephone 1876
Acoustics, variable resistance and allegations of foul play contribute to the exciting story of the invention of the telephone.
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Coaxial Cable 1929
As more and more American households acquired telephones, the pressure was on to create a better cable to accommodate the increasing demand. Engineers Lloyd Espenschied and Herman Affel answered the call.
Science4Fun
Science4 Fun: How Electricity Is Made
Read this brief article to gain an understanding of the principle of electromagnetism, how electricity is generated, and the problem with fossil fuels.
Mocomi & Anibrain Digital Technologies
Mocomi: What Is Electromagnetism?
Explains electromagnetism, the difference between a permanent magnet and an electromagnet, uses of electromagnetism, and steps for making a simple electromagnet.
Science and Mathematics Initiative for Learning Enhancement (SMILE)
Smile: Electromagnets (Grades 3 and 4)
This lesson helps students to understand the difference between magenets and electromagnets. They will also create an electromagnet.
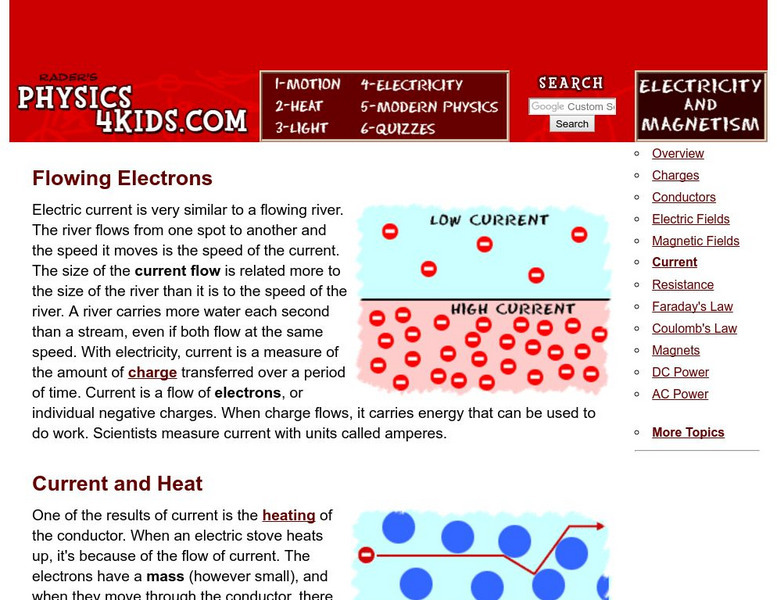
Physics4kids
Physics4 Kids: Electricity and Magnetism: Current
Explains electric current, how it produces heat, and the difference between a direct current and an alternating current.
Ducksters
Ducksters: Practice Science Questions: Easy Electronics and Magnetism
Practice science questions on the subject of easy electronics and magnetism can be found on this website.
Ducksters
Ducksters: Practice Science Answers: Easy Electronics and Magnetism
Find the answers to the science quiz on the subject of easy electronics and magnetism on this site.
Cornell University
Cornell University: Astronomy: Electromagnetism and Charge
This site from Cornell University provides a very short, very telling comparison of matter and charge. This is a good site to check out on the subject, with a chart diagram to help with further information.
Florida State University
Florida State University: The Rutherford Experiment
A simulation of the Rutherford experiment. Includes an animation and an explanation of the history behind the experiment.
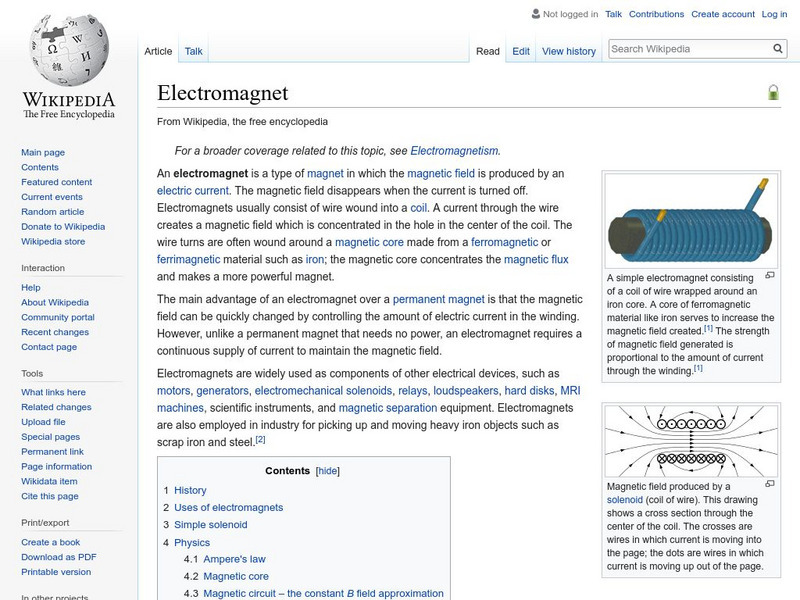
Wikimedia
Wikipedia: Electromagnet
Easy-to-read information and an illustration of an "electromagnet," a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is induced by the flow of an electric current.
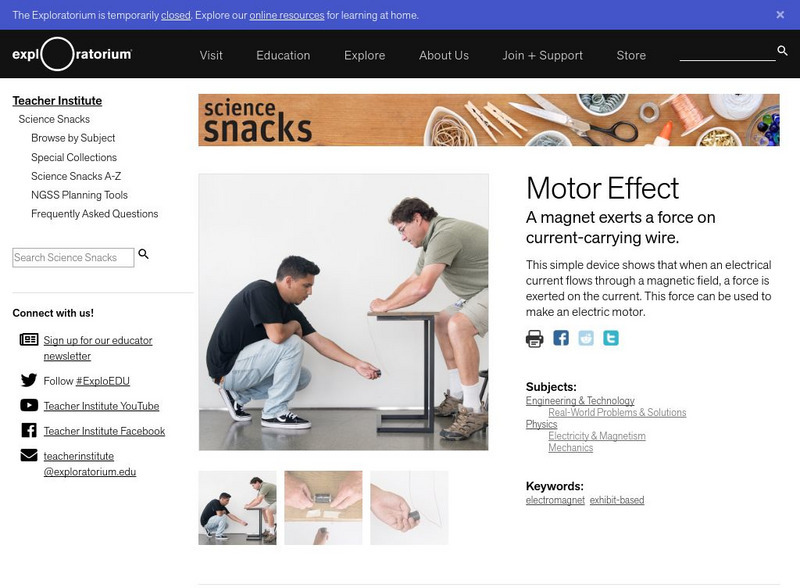
Exploratorium
Exploratorium: Science Snacks: Motor Effect
"A magnet exerts a force on current-carrying wire." This simple device shows how magnets affect wires with current in them, the basis of the electric motor. If you see, feel and understand this, the electric motor becomes very clear.
American Association of Physics Teachers
Com Padre Digital Library: Open Source Physics: Charge Trajectories
Investigate a the forces exerted on a charged particle by electric and magnetic fields. Initially, find out how the charge behaves in an electric field. Then, see how the charge behaves in a magnetic field. Finally, initiate both fields...
Concord Consortium
Concord Consortium: Stem Resources: How Electrons Move
A collection of interactive activities and games to explore how electric fields and magnetic fields move electrons and charged particles in directions that can be planned. Understand that knowing how to control the movement of electrons...
Discovery Education
Discovery Education: Build Your Own Perpetual Motion Machine [Pdf]
A lesson for students to explore the conversion of energy from electrical energy to kinetic energy by constructing a homopolar motor. Also by constructing the motor, students can investigate magnetism, electricity, and RPM.
Exploratorium
Exploratorium: Curie Temperature
In this experiment, students experience the Curie point--and what happens when a piece of iron gets too hot to attract a magnet.
Wikimedia
Wikipedia: Charles Augustin De Coulomb
Spanish-language site lets students discover the life and work of this physicist and engineer, who is known for his studies of electric charges.
American Association of Physics Teachers
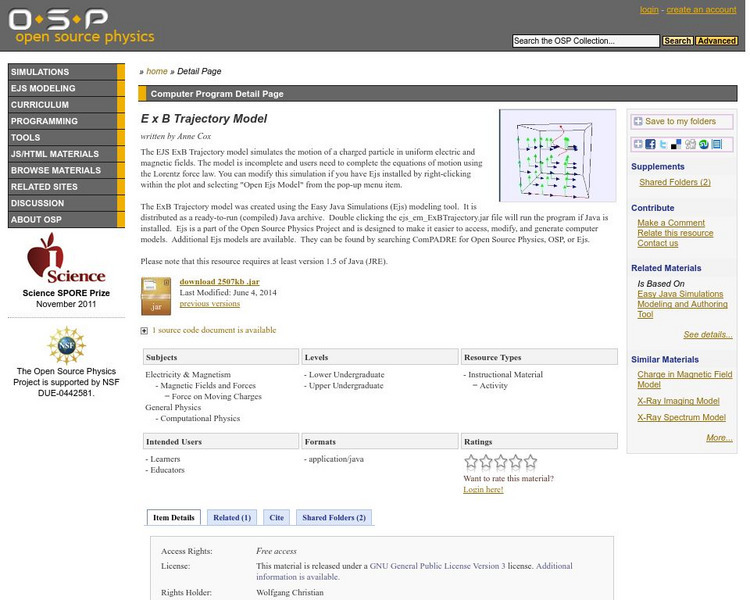
Com Padre Digital Library: Open Source Physics: E X B Trajectory Model
Simulate the motion of a charged particle in electric and magnetic fields, and then complete the equations of motion using the Lorentz force law.
TeachEngineering
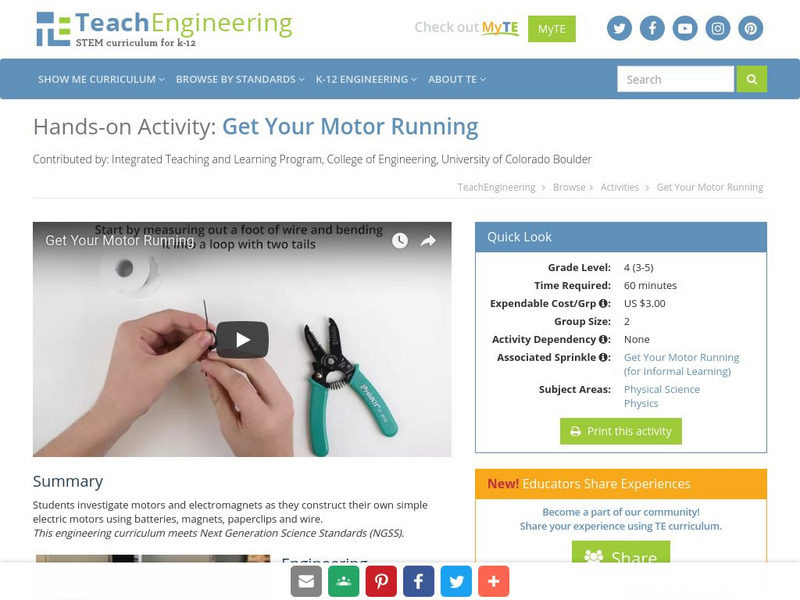
Teach Engineering: Get Your Motor Running
Students investigate motors and electromagnets as they construct their own simple electric motors using batteries, magnets, paper clips and wire.