Wolfram Research
Wolfram Science World: Pythagoras of Samos (Ca. 560 Ca. 480 Bc)
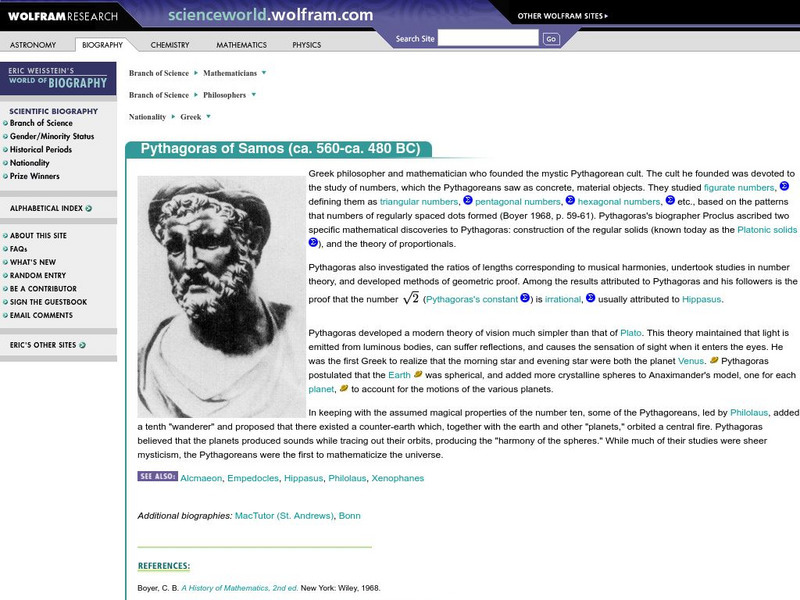
This site from ScienceWorld provides a short, informative description of many of the contributions of Pythagoras to mathematics. Links exist to some of the contributions as well as to additional information.
Philosophy Pages
Philosophy Pages: Aristotle (384 322 Bce)
The life, philosophy and metaphysics of Aristotle (384-322 BCE) are surveyed. The aim of Aristotle's logical treatises (known as the Organon) was to develop a universal method of reasoning by means of which it would be possible to learn...
Other
Aristotle
A discussion of the beliefs of Aristotle, his contributions to logic, and why he had to flee Athens at the time of Alexander's death.
Internet History Sourcebooks Project
Fordham University: Medieval Sourcebook: Al Farabi,avincenna, Averroe
This is an essay on the role of philosophy in Islam according to Al-Farabi, Avicenna, and Averroes, who are Islamic philosophers and writers from the Middle Ages.
Other
Mimesis and the Aesthetic Experience
An essay on Nietzsche's famous aesthetic of the Dionysian and the Apollonian.
New Advent
Catholic Encyclopedia: Socrates
Brief overview of Socrates' life and philosophy. Describes his philosophical method of asking questions as a "gadfly" to his fellow citizens. Author contends that Socrates proposed a version of the "teleological argument" for the...
Ducksters
Ducksters: Ancient Greek Philosophers for Kids
Kids learn about the Philosophers of Ancient Greece on this site.
University of Missouri
Famous Trials: The Trial of Socrates 399 b.c.
This looks at the historic problem of why Socrates was put on trial. The historical artifacts surrounding the trial are available online as are scholarly interpretations through the years.
Stanford University
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Political Legitimacy
Examines the concept of political legitimacy. How is it defined? What are its functions? What are the sources of political legitimacy? What does it look like in a democracy? What does it look like on a global level? These are some of the...
Stanford University
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Anaxagoras
Discusses the life of Anaxagoras of Clazomenae, his ideas about the metaphysical, the physical, the cosmos, and human intelligence, and the impact he had on later intellectuals. He is especially remembered for having been the first to...
Stanford University
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Aristotle
Looks at the life of Aristotle (384-322 B.C.E.) and the far-reaching scope of his intellectual ideas. The article examines in depth his theories in the disciplines of philosophy, politics, mathematics and science, and his legacy.
Stanford University
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Democritus
A look at the life of Democritus of Abdera. He helped to develop a theory of atomism, explained in detail here. Other significant ideas he had included his theory of perception, a theory of the soul and its relationship to living things,...
Stanford University
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Zeno of Elea
Looks at what is known about the life and work of Zeno of Elea, and explains several of his Paradoxes and how others, including Aristotle, viewed them.
Stanford University
Stanford University: Integrity
Integrity is outlined in this detailed entry by the Standford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Integrity is also explained as it relates to a variety of other characteristics. This site is designed for those looking to develop a high level of...
Stanford University
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Pythagoras
Encyclopedia article about Pythagoras from the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy that discusses not only his life, but his major contributions as well. Also includes a lengthy bibliography and links to additional information.
Stanford University
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Maimonides
A highly detailed biography of the famous Jewish philosopher and religious thinker. The article provides a thorough analysis of his religious ideas.
Stanford University
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Georg Hegel
This encyclopedia article provides an extensive overview of Hegel's life, work, and influence in philosophy.
Stanford University
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Stoicism
A detailed description of the Stoics, covering their philosophy, ethics, logic, and influence.
Stanford University
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Modal Logic
Explains modal logic by means of logical notation. Somewhat difficult for a non-specialist to appreciate. However, the introductory section does provide a general definition of "modal logic."
Stanford University
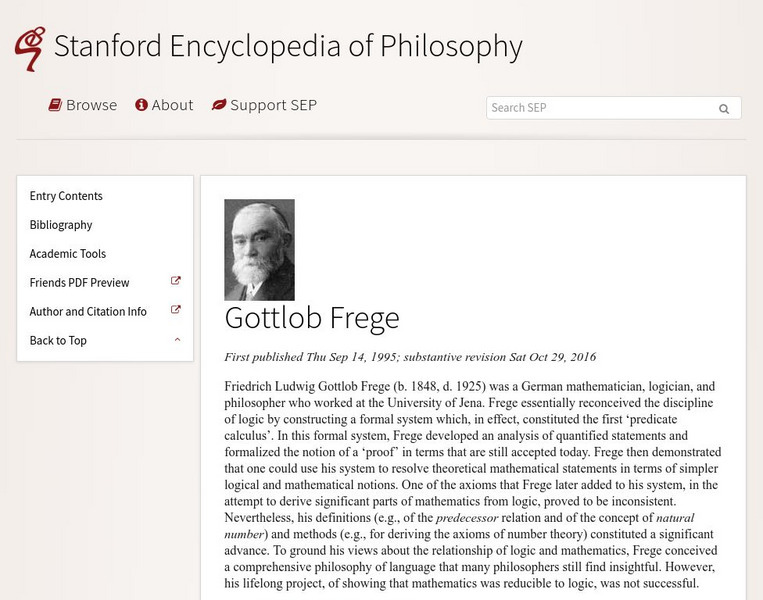
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Gottlob Frege
Good summary of Frege's thought. Some sections are more technical, but the explanation of his philosophy of language and other sections are more readable.
Stanford University
Informal Logic/stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
Describes the recent movement known as "informal logic." Summarizes its brief history, provides several detailed examples, and explains its relationship to philosophy. Bibliography included.
Stanford University
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Behaviorism
Discusses Behaviorism as a philosophy and a field of psychology. Includes information on what behaviorism is, and the types of behaviorism. Also includes links to additional information.
Stanford University
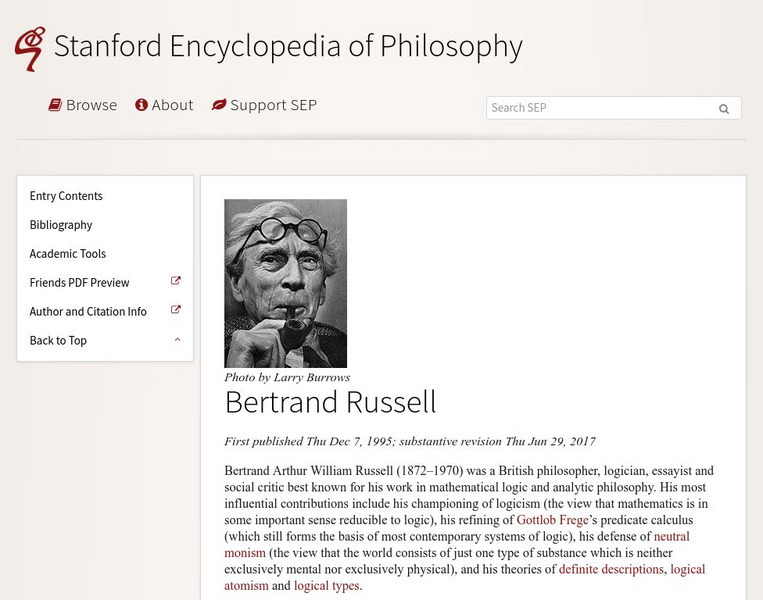
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Bertrand Russell
Excellent article summarizing Bertrand Russell's thought. Includes chronology of major events in his life, but most of the article spends time on Russell's contributions in logic, analytic philosophy, and social criticism. Also includes...
Other popular searches
- Aristotle Socrates Plato
- Socrates, Plato, Aristotle
- Platonic Solids
- Aristotle Plato
- Plato Temperance
- Platoon
- Plato Republic
- Apology Plato
- Greek Philosophy Plato
- Plato Greek Philosopher
- Plato Lesson Plans
- Platoon Film