Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Chemical and Physical Processes
In this video Paul Andersen explains the difference between chemical and physical processes. Chemical processes occur when bonds are broken and reformed. Physical processes occur when intermolecular forces are broken and reformed. A gray...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Biological and Polymer Systems
Paul Andersen explains how the structure of a biomolecule fits the function of the biomolecule. For example and enzyme must interact correctly with a substrate to lower the activation energy, The covalent and non-covalent interactions...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Entropy
Entropy is simply the dispersion of matter or energy. Paul Andersen begins with a series of video that show the natural direction of processes. According to the second law of thermodynamics the entropy may never decrease in a closed...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Spontaneous Processes
In this video, Paul Andersen discriminates between spontaneous (or thermodynamically favored) processes and those that are not spontaneous. A spontaneous process requires no external energy source. If the enthalpy change in a reaction is...
Bozeman Science
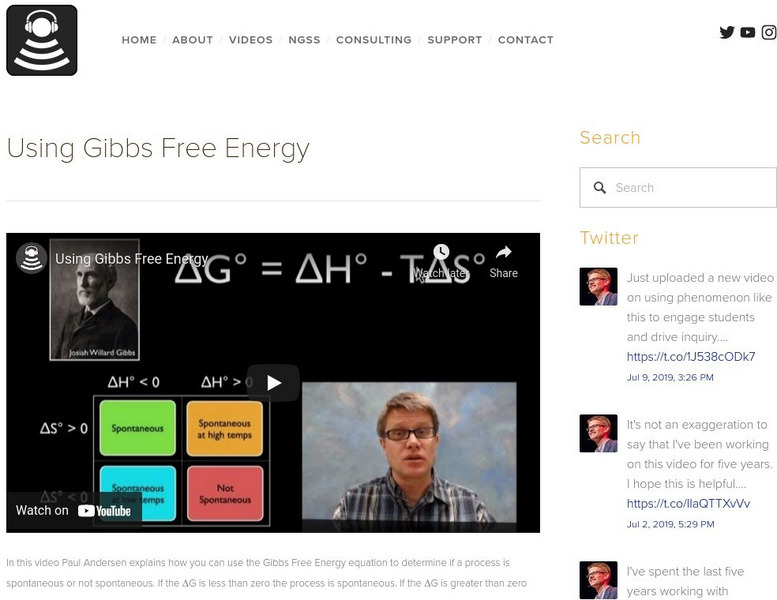
Bozeman Science: Using Gibbs Free Energy
In this video, Paul Andersen explains how you can use the Gibbs Free Energy equation to determine if a process is spontaneous or not spontaneous. Check out the concept map and slideshow to enhance study. [7:57]
Bozeman Science
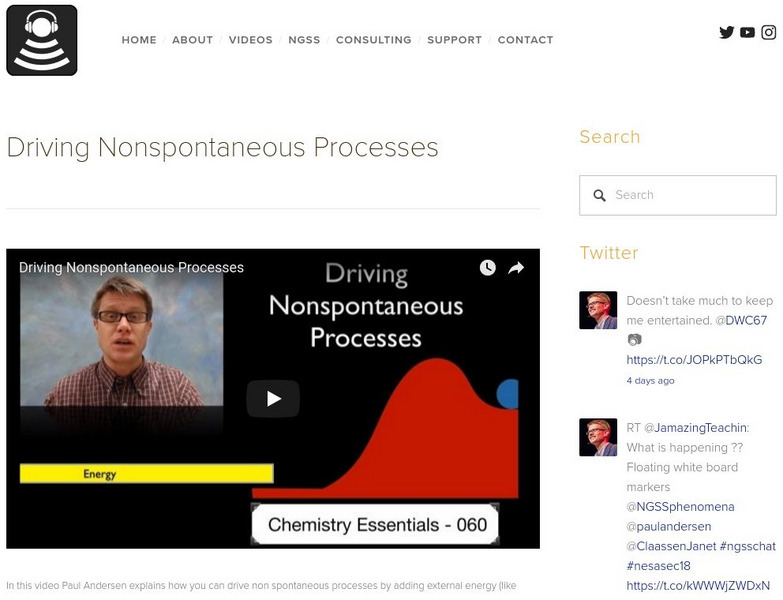
Bozeman Science: Driving Nonspontaneous Processes
In this video, Paul Andersen explains how you can drive nonspontaneous processes by adding external energy (like electricity or light) or by coupling it to a spontaneous process (like the conversion of ATP to ADP). Utilize the concept...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Kinetic Reaction Control
In this video Paul Andersen explains how a spontaneous process may take either the thermodynamically controlled or the kinetic controlled pathway. If the activation energy determines the path taken then the process is under kinetic...
Bozeman Science
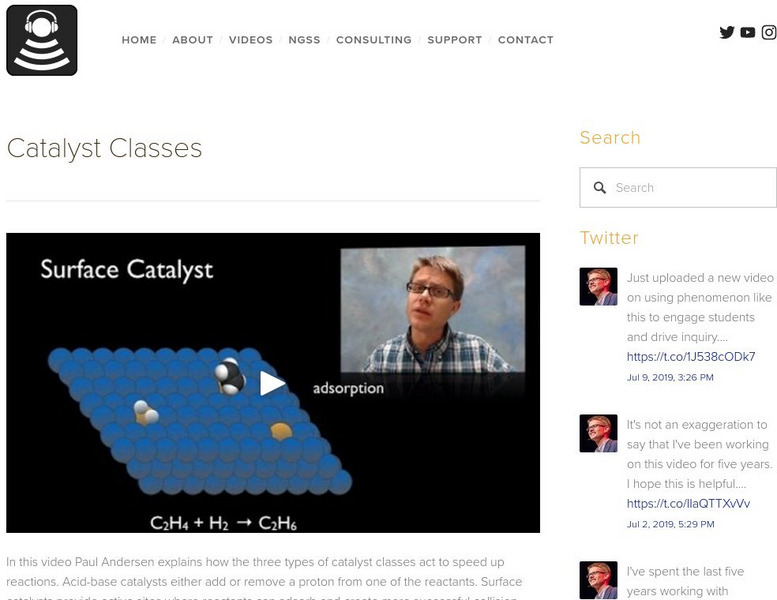
Bozeman Science: Catalyst Classes
In this video Paul Andersen explains how the three types of catalyst classes act to speed up reactions. Acid-base catalysts either add or remove a proton from one of the reactants. Surface catalysts provide active sites where reactants...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Catalysts
Paul Andersen explains how catalysts can speed up a reaction without being consumed in the reaction. Catalysts can lower the activation energy of reaction be stabilizing the transition state. They can also create new reaction pathways...
Bozeman Science
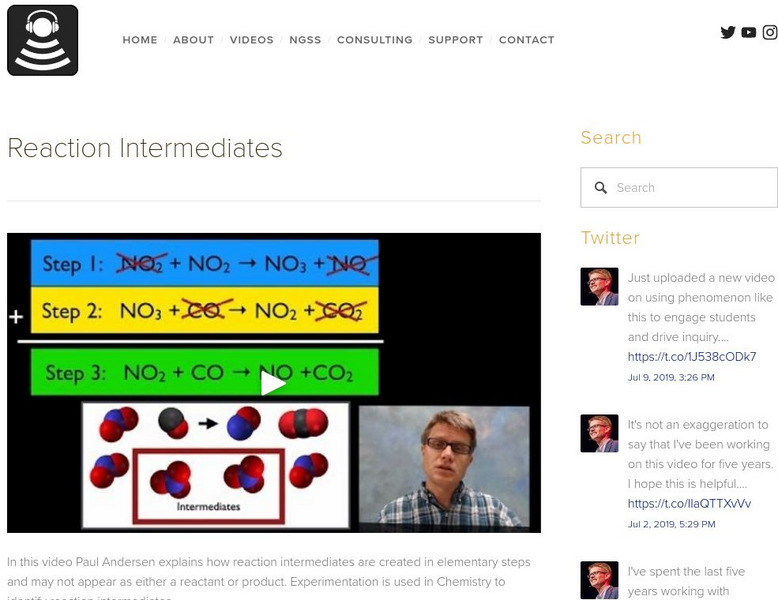
Bozeman Science: Reaction Intermediates
In this video Paul Andersen explains how reaction intermediates are created in elementary steps and may not appear as either a reactant or product. Experimentation is used in Chemistry to identify reaction intermediates. Look at the...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: The Rate Limiting Step
In this video Paul Andersen explains why the slowest elementary step in a chemical reaction is the rate-limiting step. This step can be used to determine the overall rate law of the chemical reaction. Take a look at the concept map and...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Multistep Reactions
Paul Andersen explains how an overall chemical reaction is made up of several elementary steps. The stoichiometry of this equation can be predicted but the rate law must be measured. If the elementary steps of the reaction are determined...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: The Reactions Path
In this video Paul Andersen explains how the reaction path can be described in an energy profile. Enough energy must be added to reach the activation energy required and stress the bonds. Eventually the bonds break and new bonds are...
Bozeman Science
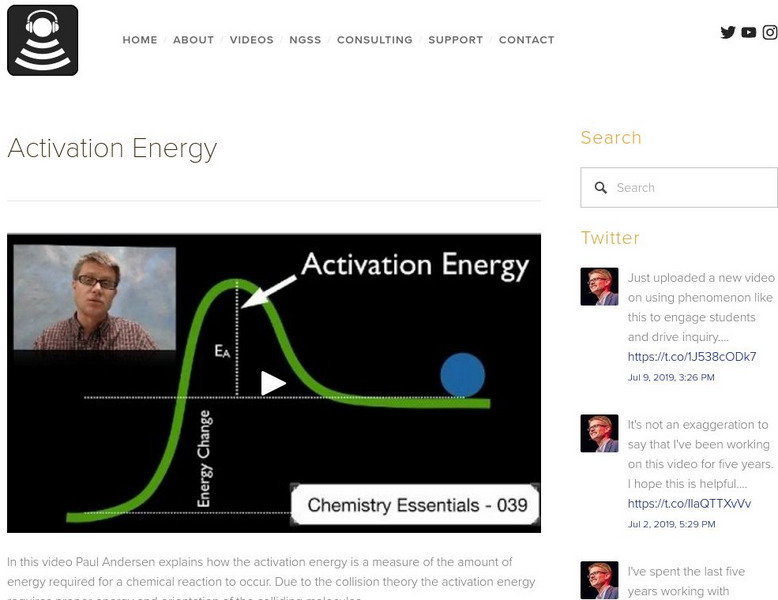
Bozeman Science: Activation Energy
In this video Paul Andersen explains how the activation energy is a measure of the amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. Due to the collision theory the activation energy requires proper energy and orientation of...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Elementary Reactions
In this video Paul Andersen explains that elementary reactions are steps within a larger reaction mechanism. Colliding molecules require sufficient energy and proper orientation to break bonds and form new bonds. A unimolecular reaction...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: The Rate Constant
In this video Paul Andersen describes the characteristics of the rate constant in chemical reactions. The rate constant is highly variable in reactions and must be determined experimentally. The rate constant is dependent on both...
Bozeman Science
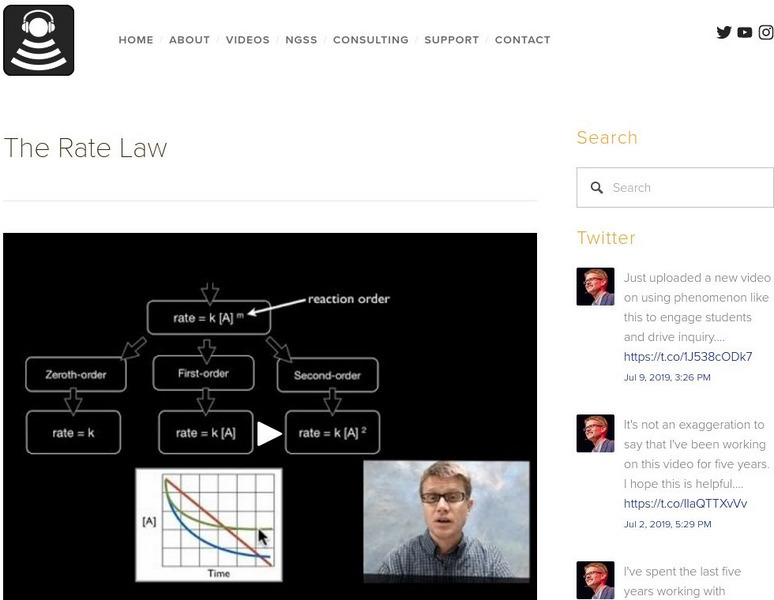
Bozeman Science: The Rate Law
Paul Andersen explains how the rate law can be used to determined the speed of a reaction over time. Zeroth-order, first-order and second-order reactions are described as well as the overall rate law of a reaction. The rate of a reaction...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Environmental Systems
Paul Andersen explains how matter and energy are conserved within the Earth's system. Matter is a closed system and energy is open to the surroundings. In natural systems steady state is maintained through feedback loops but can be...
Bozeman Science
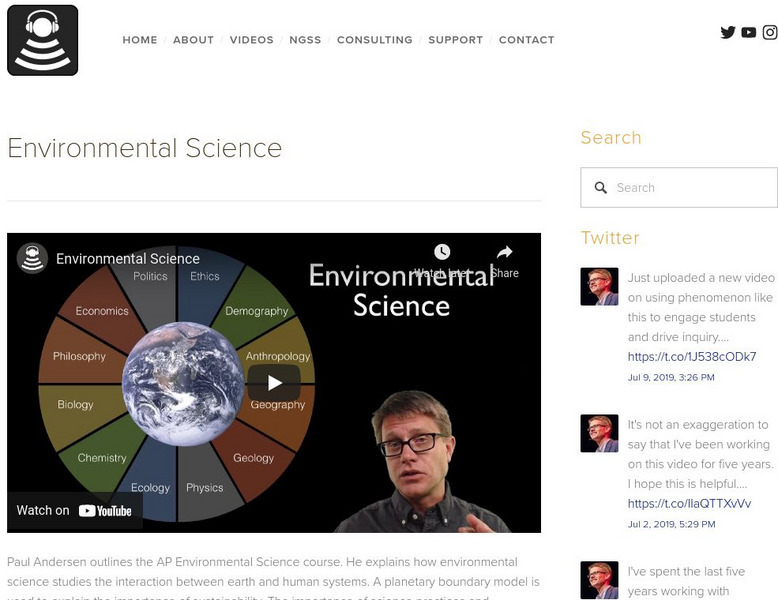
Bozeman Science: Environmental Science
Paul Andersen outlines the AP Environmental Science course through a video, concept map, and slideshow. He explains how environmental science studies the interaction between earth and human systems. A planetary boundary model is used to...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Geology
Paul Andersen explains how rock is formed and changed on the planet. The video begins with a brief description of rocks, minerals, and the rock cycle. Plate tectonics is used to describe structure near plate boundaries. Hot spots and...
Bozeman Science
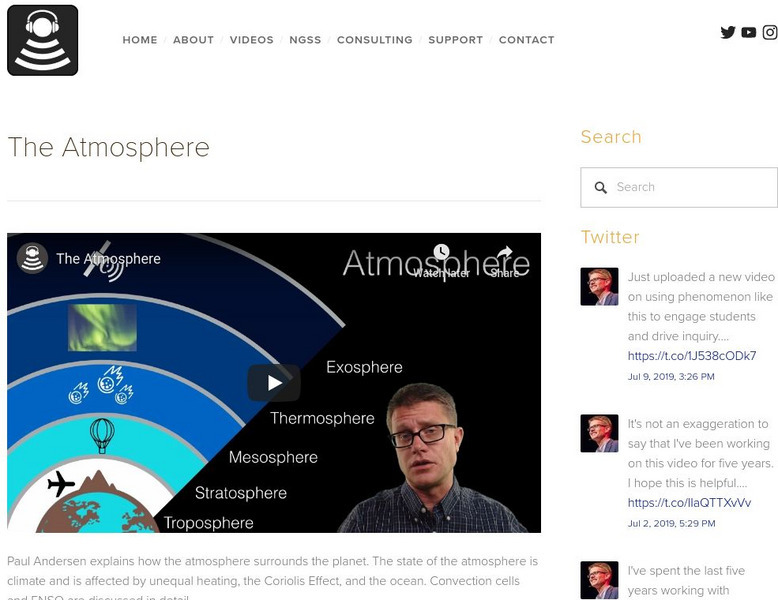
Bozeman Science: The Atmosphere
Paul Andersen explains how the atmosphere surrounds the planet. The state of the atmosphere is climate and is affected by unequal heating, the Coriolis Effect, and the ocean. Convection cells and ENSO are discussed in detail. Take...
Bozeman Science
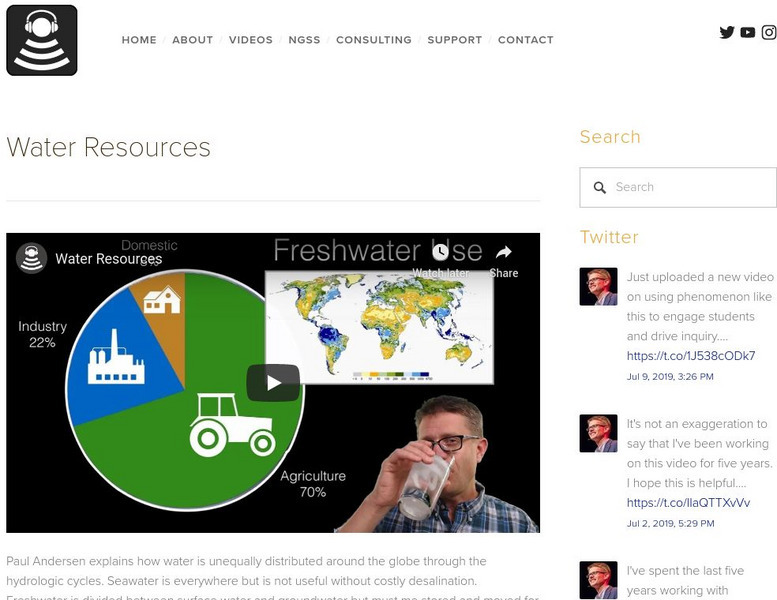
Bozeman Science: Water Resource
Paul Andersen explains how water is unequally distributed around the globe through the hydrologic cycles. Seawater is everywhere but is not useful without costly desalination. Freshwater is divided between surface water and groundwater...
Bozeman Science
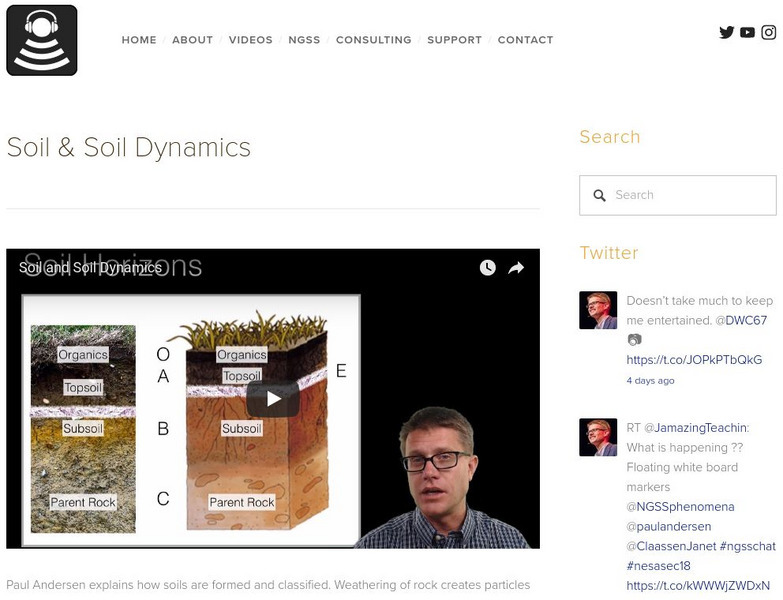
Bozeman Science: Soil and Soil Dynamics
Paul Andersen explains how soils are formed and classified. Weathering of rock creates particles which are mixed with water, air, and organic material. Soils are classified according to particle size, chemical makeup, and horizon...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ecosystem Ecology
Paul Andersen explains how ecosystems function. He begins with a description of how life on the planet is ordered from large to small in biomes, ecosystems, communities, population, and individuals. He describes the major terrestrial and...