Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Rate of Reaction
Definition of reaction rate, and examples of calculating the average rate of reaction. [9:09]
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Finding Units of Rate Constant K
Discover how to find the units for the rate constant k for a zero, first, or second order reaction. [5:05]
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Half Life of a First Order Reaction
Understand how to derive the half-life equation of a first-order reaction starting from the integrated rate law. [8:12]
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Half Life of a Second Order Reaction
Recognize how to derive half-life equation of a second-order reaction starting from the integrated rate law. [7:04]
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Zero Order Reaction (With Calculus)
Understand the process of deriving the integrated rate law for zero-order reactions using calculus. Identify how to graph zero order rate data to see a linear relationship. [9:46]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Elementary Reactions
In this video Paul Andersen explains that elementary reactions are steps within a larger reaction mechanism. Colliding molecules require sufficient energy and proper orientation to break bonds and form new bonds. A unimolecular reaction...
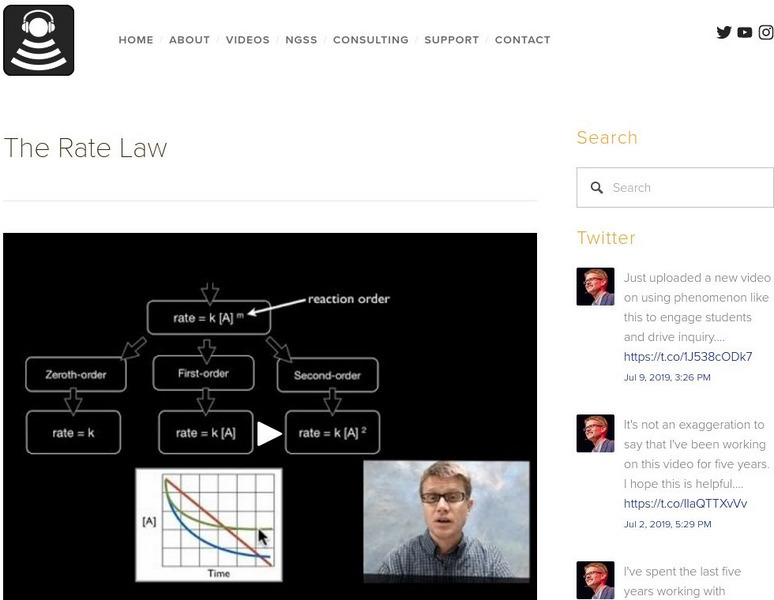
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: The Rate Law
Paul Andersen explains how the rate law can be used to determined the speed of a reaction over time. Zeroth-order, first-order and second-order reactions are described as well as the overall rate law of a reaction. The rate of a reaction...
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Chemistry: Keq Intuition
A video lecture showing how the equilibrium constant is derived. Understand how equilibrium in a reaction is reached when the forward reaction rate equals the reverse reaction rate. The video explores how knowing the concentrations of...
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Ap Chemistry: The Rate of Reactions
Paul Andersen defines the rate of a reaction as the number of reactants that are consumed during a given period of time. The rate of the reaction can be affected by the type of reaction as well as the concentration, pressure, temperature...