Khan Academy
Khan Academy: 2015 Ap Chemistry Free Response 2 C
Explanation of Gibbs free energy and equilibrium constant of dehydration. Example is from the 2015 AP chemistry test. [12:23]
Bozeman Science
Bozeman Science: Thermodynamics and P v Diagrams
In this video Paul Andersen explains how the First Law of Thermodynamics applies to an ideal gas in a piston. A pressure-volume graph can be used to determine the type of thermodynamic process. Included is a discussion of and P-V diagram...
Bozeman Science
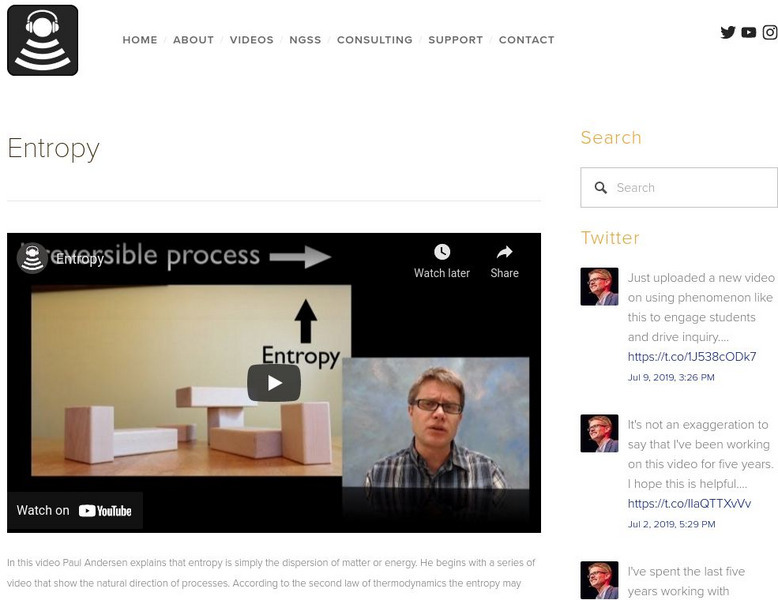
Bozeman Science: Entropy
Entropy is simply the dispersion of matter or energy. Paul Andersen begins with a series of video that show the natural direction of processes. According to the second law of thermodynamics the entropy may never decrease in a closed...
Bozeman Science
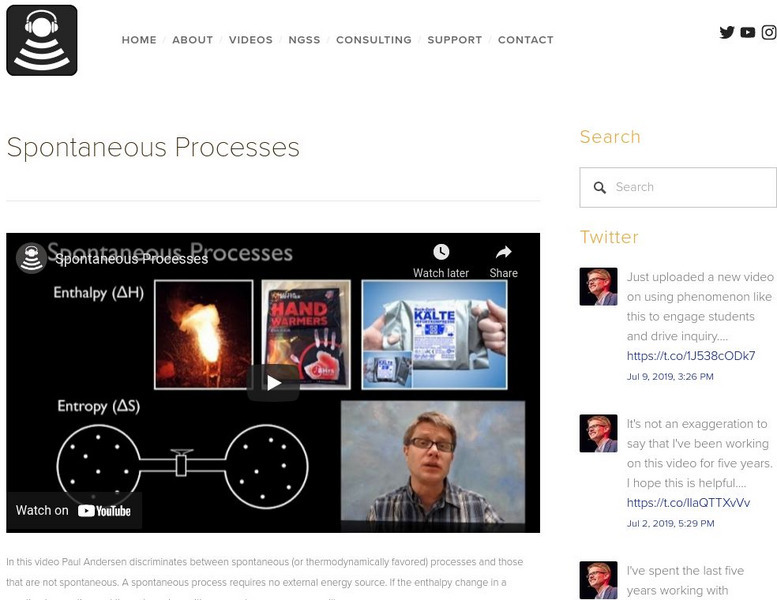
Bozeman Science: Spontaneous Processes
In this video, Paul Andersen discriminates between spontaneous (or thermodynamically favored) processes and those that are not spontaneous. A spontaneous process requires no external energy source. If the enthalpy change in a reaction is...
Bozeman Science
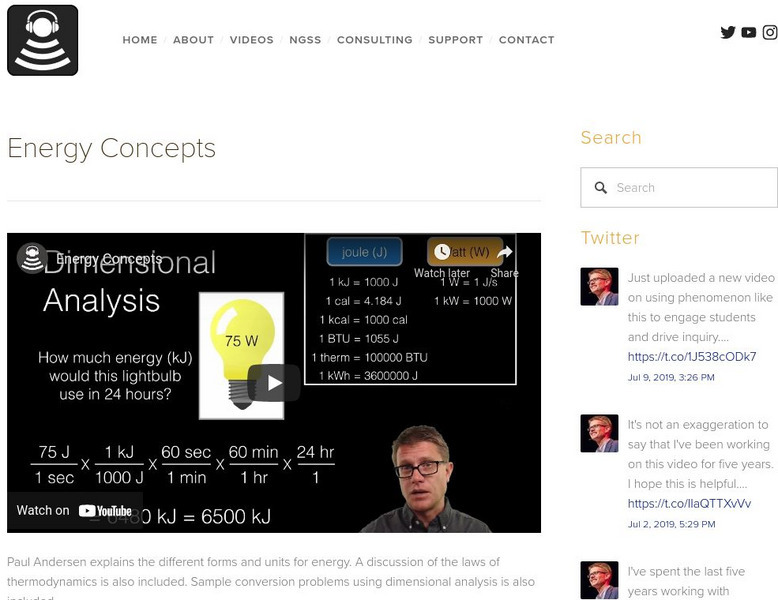
Bozeman Science: Energy Concepts
Paul Andersen explains the different forms and units for energy. A discussion of the laws of thermodynamics is also included. Sample conversion problems using dimensional analysis is also included. Utilize the practice problems and...
Sophia Learning
Sophia: 1st Law: Conservation of Energy
This lesson will define the first law of thermodynamics, and use examples to illustrate conservation of energy.
Crash Course
Crash Course Chemistry #13: Ideal Gas Problems
Find put how the ideal gas "law" often becomes little more than the ideal gas estimate when it comes to what gases do naturally. But it's a close enough estimate in enough situations that it's very valuable to know. In this episode, Hank...
Crash Course
Crash Course Chemistry #12: The Ideal Gas Law
Gases are everywhere, and this is good news and bad news for chemists. The good news: when they are behaving themselves, it's extremely easy to describe their behavior theoretically, experimentally and mathematically. The bad news is...
Crash Course
Crash Course Chemistry #14: Real Gases
Hank bursts our ideal gas law bubble, and brings us back to reality, explaining how the constants in the gas law aren't all that constant; how the ideal gas law we've spent the past two weeks with has to be corrected for volume because...
Crash Course
Crash Course Physics #23: Thermodynamics
Have you ever heard of a Perpetual Motion Machine? More to the point, have you ever heard of why Perpetual Motion Machines are impossible? One of the reasons is because of the first law of thermodynamics! In this video [10:04] episode of...
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Chemistry: Macrostates and Microstates
A video lecture exploring the difference between macrostates, microstates, and thermodynamic equilibrium. Understand how macrostates is best defined when the system is in thermal equilibrium and describes pressure, temperature, and...
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Thermodynamics: Stoichiometry Example Problem 1
Figuring grams of reactants and product produced from reaction of phosphorous and chlorine.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Chemistry: Quasi Static and Reversible Processes
Understand that an almost static process is called quasi-static process in this video lecture. Also explained is how all reversible processes are quasi-static but not all quasi-static processes are reversible. Video lecture gives...
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Thermodynamics: Proving That It Is the Most Efficient
Proving that a Carnot Engine is the most efficient engine
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Thermodynamics: Efficiency of a Carnot Engine
Definition of efficiency for a heat engine. Efficiency of a Carnot Engine.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Chemistry: Thermodynamics and Entropy
A video lecture discussing the definition of entropy as the change of states and as the heat added to the system divided by the temperature added. The video reconciles these two definitions by going through examples to explain how they...
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics (Part 4)
An introduction to the concept of a mole and its role in the field of thermodynamics. Using a periodic table, one learns how to calculate the number of moles a quantity of an element has, based on its atomic mass. Goes on to explain how...
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics (Part 3)
An introduction to Kelvin. Example of a problem involving the ideal gas law.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics (Part 1)
Discussion of how gases generate pressure in a container and why pressure times volume is proportional to the combined kinetic energy of the molecules in the volume. [9:49]
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics (Part 5)
Demonstrates an example problem involving the formula PV=nRT. After calculating how many moles, he uses Avogadro's Number of molecules per mole, to calculate how many atoms that amount would represent. [8:00in]
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics (Part 2)
Example problem where P1V1=P2V2. Includes an introduction to temperature. [10:08]
Sophia Learning
Sophia: 2nd Law: Entropy
This lesson will introduce the second law of thermodynamics and define the term entropy, providing examples of entropy.
Crash Course
Crash Course Chemistry #18: Enthalpy
A crash course episode introducing what the state function is, and how it varies from a path-dependent function; why enthalpy change is different from heat; and the fact that bonds are energy and to form and break them they release and...
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Chemistry: First Law of Thermodynamics/internal Energy
A video lecture defining the first law of thermodynamics and internal energy. Understand that energy is only transferred from one form to another and not created or destroyed. Also learn how measure the amount of energy something has as...