Energy4Me
Energy4me: Reservoirs and Production
The students will learn that porosity refers to the percentage of holes (pores) in the rock. Permeability is the ability of fluids to travel through porous rocks. If a well is to be successfully produced, the reservoir must have...
Other
Garden With Insight: Porosity
A good description of soil porosity and how it is measured. There are links to mixing soil, aerating soil, and soil settling with rain.
Idaho State University
Idaho State University: Groundwater Process, Supply, and Use
Understand the vulnerability to polltuion the supply of drinking water in the United States has. Know what aquifers are and how groundwater is moved. Identify Darcy's Law and know how to apply it.
Other
Schlumberger Excellence in Education Development: The Permeability of Soil
This resource includes an experiment to show where rainwater goes. Discover the different layers of soil and what each layer is made of.
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: The Other Water Cycle
For students that have already been introduced to the water cycle, this instructional activity is intended as a logical follow-up. Students will learn about human impacts on the water cycle that create a pathway for pollutants beginning...
Science Buddies
Science Buddies: Porosity and Particle Size
Often, when we think of something that is solid we think about rocks. But in reality, rocks have tiny holes of air inside them. This is called porosity. In this experiment you can find out what it means to be "solid as a rock."
American Geosciences Institute
American Geosciences Institute: Earth Science Week: Exploring Porosity
Experiment to find out which size of gravel has the most porosity by measuring volume.
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: How Full Is Full?
During this activity, students will learn about porosity and permeability and relate these concepts to groundwater flow. Students will use simple materials to conduct a porosity experiment and use the information to understand how...
TeachEngineering
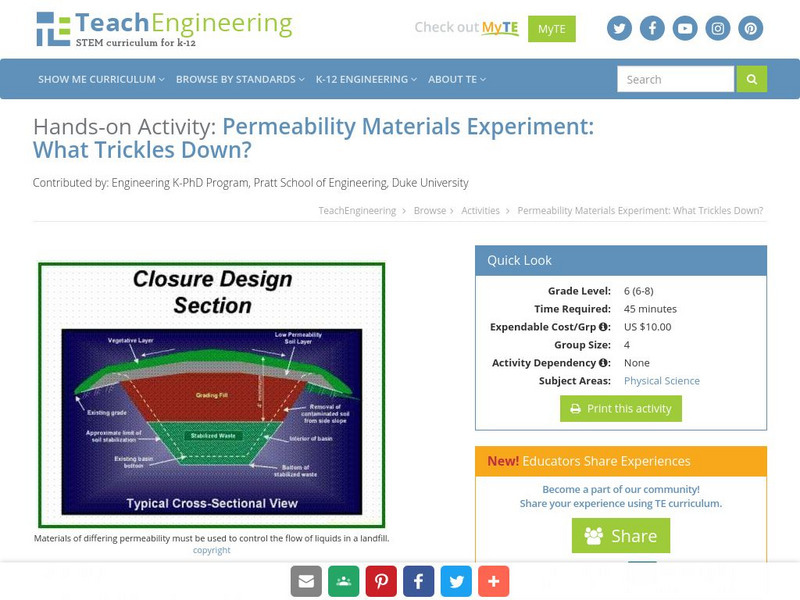
Teach Engineering: What Trickles Down?
Permeability is the degree to which water or other liquids are able to flow through a material. Different substances such as soil, gravel, sand, and asphalt have varying levels of permeability. In this activity, students will explore...
American Geosciences Institute
American Geosciences Institute: Earth Science Week: Measuring Permeabilities of Soil, Sand, and Gravel
This investigation will help students learn that different geologic materials have different characteristics.
TeachEngineering
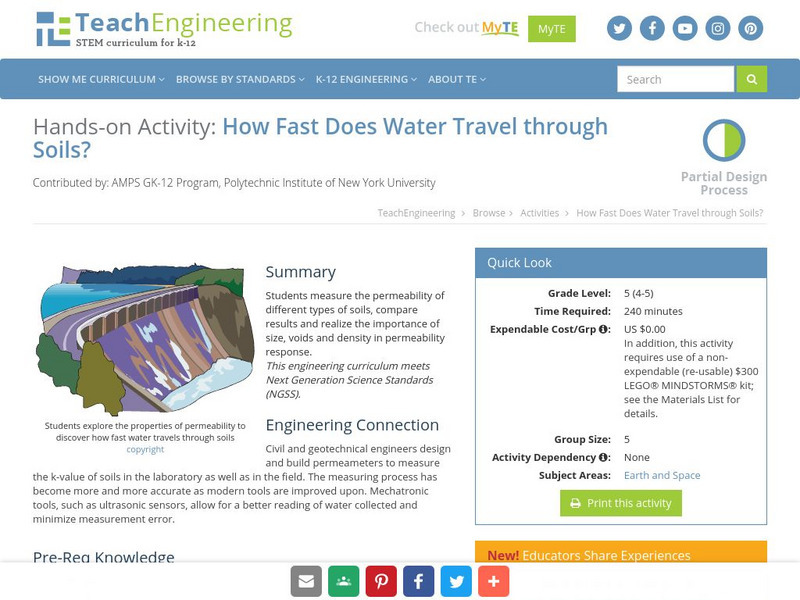
Teach Engineering: How Fast Does Water Travel Through Soils?
Students measure the permeability of different types of soils, compare results and realize the importance of size, voids and density in permeability response.
American Geosciences Institute
American Geosciences Institute: Earth Science Week: Soil Properties
Students investigate soil porosity by building a model using the three main soil textures: sand, silt, and clay.
Cornell Lab of Ornithology
Habitat Network: Pavement or Gravel
Find out how gravel and pavement can be beneficial to a backyard ecosystem.
US Geological Survey
Usgs: Ground Water Aquifers
Resource is a brief explanation of an aquifer and how they work. This article also touches upon artesian wells. A picture and a fun activity to illustrate the concept of an artesian well are included. Click Home to access the site in...
American Geosciences Institute
American Geosciences Institute: Earth Science Week: Groundwater Movement
Students learn how water moves through rock materials such as sand, gravel, and clay.
TeachEngineering
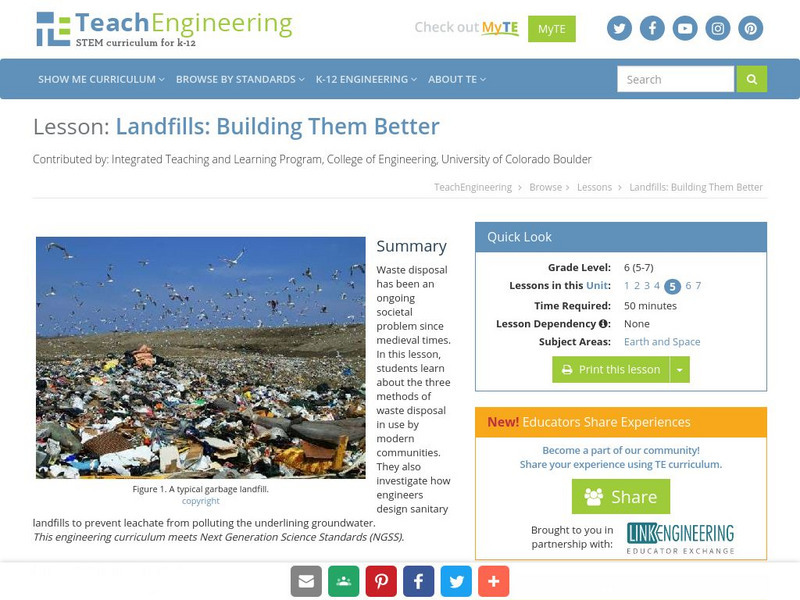
Teach Engineering: Landfills: Building Them Better
Waste disposal has been an ongoing problem since medieval times. Environmental engineers are employed to develop technologies to dispose of the enormous amount of trash produced in the United States. For this lesson, students will learn...